ESG
ISO 50001 Energy Management System
The Definition of ISO 50001 Energy Management System
ISO 50001 is Energy Management System (EnMS in abbreviation). The goal of ISO 50001 EnMS is to reduce the cost of enterprises and improve environmental issues by decreasing energy consumption. In order to solve the impact that comes from the substantial energy consumption and climate change the global, by establishing Energy Management System, enterprises think outside the box of the energy cost on energy performance management to improve the use efficiency of enterprises and to reduce the emission of greenhouse gas for saving the cost of energy consumption of enterprises. Besides, for reducing the various impact on the environment caused by the operation of an enterprise.
The Importance of ISO 50001 Energy Management System
ISO was first released in June 2011. Now the latest version is ISO 50001:2008 EnMS which was released on Dec. 21, 2018.
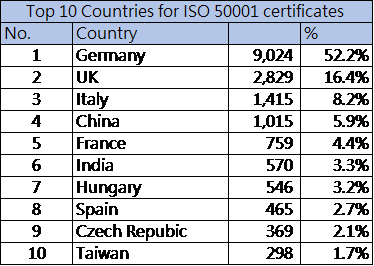
According to the data in 2016, the top five countries that acquire the most ISO 50001 certificates are Germany, the United Kingdom, Italy, China, and France. Four of these five countries are located in Europe, which means ISO 50001 EnMS in European countries has been a practical action, not a symbolic indicator. As of the end of 2017, 22,870 companies around the world have passed the verification of this standard. Europe gets the highest ratio for passing the verification, and the following is in Asia. More and more companies include ISO 50001 EnMS in their sustainable development strategies, which strengthens the requests to suppliers for adapting to the changes in the energy supply environment. If the rise of awareness is happening, the ISO 50001 EnMS can be developed extensively.
ISO 50001:2018 EnMS's Main Principles
-
ISO 50001 EnMS is already compatible with the existing standard management system of an enterprise. For instance, the company has an ISO 9001 quality management system and an ISO 14001 Environmental Management System which can smooth the process of ISO 50001 implementation.
-
The company uses the PDCA circle to improve its work routine continuously. The principles of the PDCA circle are -
-
Plan: Proceeding the physical examination of the departments and machines in the entire factory. To analyze the distribution situation of energy consumption of the production facility, and to formulate the action plan for energy-saving and carbon reduction as per the needs of each unit. -
Do: Based on the plans for energy-saving and carbon reduction, the actions for each department are to carry out the staff training, and replace old facilities with new ones, etc. -
Check: The duty of a supervisor is to confirm the actual improved situation with each department head and staff together. -
Action: Modify the action plan for energy-saving and carbon reduction anytime to make sure the plans of each department achieve the best outcome. If a problem needs to be addressed, it has to be proposed immediately and then to be executed after the review.
-
ISO 50001 is used to establish, supervise, document, and provide energy reports for predicting greenhouse gas emissions and finding out solutions.
Assist enterprises to optimize energy management and reinforce good management behavior.
-
Evaluate and determine the use of new energy that includes the potential energy, the use of renewable energy, the development of alternative energy, etc.
The Example of Acquiring ISO 50001 Energy Management System
Layana completed the audit of ISO 50001:2018 EnMS in 2019. By making itself an example, Layana implements energy management in the operation of the entire factory and shares it with supplies and clients. Layana’s indicator for energy management is as the following:
Conclusion
Economic growth plays a vital element in a country; however, while pursuing economic development, humans may unconsciously sacrifice the natural environment and ecology. Although Mother Earth does not protest in time, it accumulates over a period of time damage, it eventually leads to counterattacks. For example, the hole in the ozone layer, global warming, and the melting of icebergs at the South Pole and the North Pole.
ISO 50001 EnMS certification helps companies to take sustainability into consideration when pursuing margin profits and sales revenues. In the 21st century, we have to utilize the existing resource effectively which can be passed down the benefits to the next generations.
Article reference source: 22,870 data in 2017/ Top 10 Countries for ISO certificates/ Production & Ecology & Life chart reference to Xie Xhencheng at SGS Taiwan Limited.
ISO 50001-2018 introduction for a new version of energy management system standard.pdf
Environmental and Energy Policies
Since its establishment in 1982, Layana has been dedicated to nurturing high-quality partnerships with suppliers and clients. We strive to provide our employees with a conducive environment for their well-being and ongoing personal growth. In pursuit of sustainable business practices and the establishment of rigorous standards for environmental impact management, we have implemented the ISO 50001 Energy Management System. We hold in high regard the responsible utilization of all forms of energy, actively champion energy-saving initiatives. All colleagues collectively drive the ISO 14064 Greenhouse Gases, taking tangible steps towards energy conservation and fulfilling our obligations as responsible global citizens, thereby laying the foundation for continuous improvement in the future. We hereby commit to and persistently advocate for the following initiatives:
Environmental Policy
- Regulatory Compliance: We ensure that all our production activities strictly adhere to regulatory requirements. Our commitment lies in driving green supply chains and offering environmentally friendly products. Through continuous improvement of our work environment, we aim to achieve the goal of zero occupational accidents.
- Environmental Protection: We prioritize product designs with low toxicity and easy disassembly, conduct thorough carbon footprint assessments, practice resource conservation, industrial waste reduction, pollution prevention, and enhance control over hazardous substances. Our objective is to minimize our environmental impact.
- Resource Optimization: We place great emphasis on personnel education and training, fostering a culture of continuous improvement within our operations. By doing so, we strive for sustainable development and contribute to a greener future.
Energy Policy
- Regulatory Compliance: We provide energy improvement resources and diligently implement energy laws and regulations to ensure compliance at all times.
- Enhancing Energy Efficiency: We actively seek equipment procurement with energy-saving certifications and integrate energy-saving designs and processes into our operations. Our aim is to achieve significant energy savings and meet our targets.
- Inclusive Engagement: We believe in creating an energy-conscious organization where everyone plays a part. Through the establishment of effective energy strategies and the active involvement of all employees, we drive sustainable business practices.
- Continuous Improvement: We consistently strive for betterment by implementing material conservation designs, reducing energy consumption, and optimizing energy usage efficiency.
Green Factory
What is a green factory?
| A green factory refers to a manufacturing facility that prioritizes environmental sustainability in its production processes, products, and infrastructure, surpassing the standards set by traditional factories. In the face of climate change, green factories serve as a vital solution within the industrial sector. The primary objective of a green factory is to demonstrate respect for the environment by diligently working towards reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste generation, and optimizing energy consumption during the manufacturing of products.
Typically, green factory certification is bestowed by governmental authorities, acknowledging companies that invest in creating eco-friendly facilities that provide a healthy and comfortable working environment for employees, all while reducing their carbon footprint. Accreditation bodies for green factories conduct comprehensive audits encompassing various aspects of the production process. These aspects encompass the efficiency of industrial equipment, energy optimization of cooling and heating systems, waste management and recycling practices, water resource management, sustainability of inputs, carbon emission reduction associated with logistics demands, energy consumption for factory lighting, energy efficiency, and risk mitigation considerations in architectural designs.
The establishment of a green factory necessitates coordination and collective efforts across all internal departments of a company, fostering a shared understanding of the essential principles that drive green manufacturing practices. Active engagement of departments and employees enables the identification of areas with potential inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement, thereby facilitating the development of innovative solutions to enhance factory efficiency while minimizing or eliminating waste. |
How to become a green factory?
|
Becoming a green factory involves meeting two essential criteria:
Only when these two factors are successfully integrated can a factory truly be considered green. In essence, the realization of a green factory requires a dual focus on creating environmentally friendly infrastructure and implementing sustainable production practices. |
The fundamental steps to obtain Green Factory certification are outlined below:
- Set mid-term objectives to transform your factory into an environmentally sustainable facility, either through construction or renovation.
- Develop a comprehensive plan focusing on addressing sustainability issues related to the establishment of green factory infrastructure and production processes.
- Create a roadmap for the future by establishing measurable standards and target completion dates for each stage. For instance, goals may include reducing water loss by 10% following the installation of new equipment, achieving a 20% decrease in energy consumption for a specific process after completion, and completely eliminating the use of highly polluting materials.
- Establish a dedicated team responsible for coordinating and making decisions regarding the implementation of improvement plans across various departments.
- Formulate teams to handle infrastructure planning and clean production planning. Effective communication between these teams is crucial to understanding project requirements and progress.
- Conduct regular meetings to ensure alignment within the company. During these meetings, assess the feasibility of proposed plans, approve or reject their implementation, and analyze the progress and outcomes of previous initiatives.
- Consider necessary permits or approvals before commencing construction and manage them accordingly. Take into account pre-building requirements such as zoning regulations, environmental agreements, seismic and stormwater management, drawings, or projects approved by relevant government agencies or institutions.
- It is highly recommended to engage experienced construction companies and architectural design firms with expertise in constructing environmentally sustainable facilities.
- Identify the environmental requirements that the construction company must adhere to when building a new factory or renovating an existing one. Additionally, conduct periodic audits of the construction work to ensure compliance with these requirements, which may include measures such as preventing the release of dust or pollutants into the atmosphere and implementing waste reduction and recycling practices.
- Once the new factory infrastructure is completed and new equipment is installed or existing equipment is improved, validate the production capabilities within the facility. Make any necessary adjustments until the desired production levels are achieved.
The Impact of Green Factories
When evaluating the impact of constructing green factories, it is crucial to identify the entities affected by this impact.
- The foremost and most significant impact is on the environment. By opting for the construction of green factories instead of more polluting traditional alternatives, not only do we avoid air, water, or environmental pollution, but we also strive to minimize potential damage to the environment, particularly the disruption of animal and plant populations. Furthermore, green factories are designed to ensure responsible usage of local natural resources.
- There is a positive and substantial impact on the health and well-being of employees. The design of green factories takes into account the working environment, including measures such as providing an adequate number of mobile restrooms and reducing workplace carbon emissions. This not only reduces the probability of work-related accidents but also significantly improves the overall working conditions for employees. Moreover, when employees' health and happiness improve, it extends to the well-being of their families.
- The establishment of green factories contributes to the advancement of industrial capabilities in urban areas. Green factories exhibit resilience in the face of future challenges or crises. Additionally, they alleviate the strain on the region's power systems and water resources, as their resource consumption is significantly lower compared to traditional construction practices.
- Green factories have a positive impact on local residents. Apart from integrating corporate social responsibility initiatives aligned with green factory designs, the employment opportunities offered by companies committed to sustainable development without compromising the local ecosystem also increase. Furthermore, by setting examples of businesses dedicated to environmental and human well-being, it fosters a positive influence on future entrepreneurs.
- Obtaining green factory certification not only adds value to the company but also creates value within the production and manufacturing processes. Green factories enhance the company's reputation, provide tax benefits, and reduce production costs, ultimately making the company more competitive and improving its business prospects.
The Challenges and Opportunities of Embracing a Green Factory
Constructing a green factory comes with numerous advantages, but it also presents challenges and risks that not all companies are willing to undertake.
Despite a company's significant efforts to enhance production and incorporate eco-friendly building practices, obtaining certification may not always be feasible. Alternatively, even if certification is eventually achieved, it may require more time and financial resources than initially anticipated. To mitigate such situations, Layana suggests that the decision to establish a green factory should be driven by the company's genuine environmental consciousness, rather than solely being motivated by the ambition to acquire a certificate. The certification serves as a powerful instrument, affirming that the company is making sound decisions and taking meaningful steps towards achieving its objectives.
Furthermore, the requirements, indicators, recommended materials, and production standards necessary for compliance may evolve over time, necessitating future modifications and enhancements. To address this, Layana recommends that companies internally adopt a policy of continuous improvement, surpassing the requirements outlined in certification systems or legal frameworks related to environmental sustainability.
Additionally, the construction of a green factory entails extensive planning, seamless team coordination, resource allocation, and meticulous auditing. Consequently, unwavering commitment is essential, ensuring that the company remains dedicated to these principles over the long term. On one hand, a company opting for a green factory showcases its leadership and forward-thinking approach, thereby bolstering its reputation. On the other hand, official certification as a green factory serves as tangible evidence of the company's unwavering dedication and significant progress. Consequently, such a company cannot be accused of mere "greenwashing," as the green factory certification necessitates a comprehensive evaluation by the supervisory authorities.
Taiwan's Green Factory Certification System
In Taiwan, the Green Factory Certification stands as an advanced standard for recognizing environmentally sustainable buildings. The Industrial Development Bureau of the Ministry of Economic Affairs is responsible for awarding this esteemed certification. The Taiwan Green Factory label is recognized worldwide as a groundbreaking initiative, honoring companies that prioritize clean production practices in their factory designs. These practices encompass energy and water efficiency, waste reduction or elimination, pollution prevention, employee well-being through improved workplace conditions, protection of surrounding ecosystems, and commitment to corporate social responsibility. The Green Factory assessment evaluates whether the factory's building itself meets green building criteria and if its internal production processes adhere to clean production standards.
Layana strives to embody environmental friendliness while adhering to international environmental standards. In addition to integrating natural and green elements into our building structures, we have implemented scalable recycling systems and lush green gardens in our factory space designs. We champion energy-saving and carbon reduction measures by employing energy-efficient lighting and air conditioning systems in our day-to-day operations, along with measures to reduce CO2 emissions within our facilities. Our ultimate goal is to minimize the environmental impact of our factory and production processes, bolster the industry's commitment to sustainability, and achieve carbon neutrality.
LAYANA has obtained the Green Factory Certification and has passed the evaluation of the Cleaner Production System.
|
2022 Taiwan's Green Factory Label Celebrates 10th Anniversary |
Green Factory Certification |
Green Factory Certification |
The History of our Green Building Factory
|
|
|||||||||
April 2014Start of design phase Obtained building permit |
September 2015Inauguration Ceremony |
July 2016Coronation Ceremony |
November 2017Obtained Green Building Candidate Certificate |
February 2018Factory Registration Certificate |
August 2019Obtained Gold-Level Green Building Certificate |
September 2021Obtained Carbon Footprint Label |
January 20221. Obtained Cleaner Production System Certificate 2. Obtained Green Factory Mark |
2024Obtained ISO 14064-1 Greenhouse Gas Certification |
2025Renewal of Cleaner Production System Certificate & Green Factory Mark |
Conclusion
The Green Factory Certification Label is not only a recognition of the company's team members, but also a way to give back to the natural environment on which humanity depends. The process of achieving a green factory, from Green Building and Clean Production to obtaining the Green Factory Certification, involves guidance, implementation, adjustments, audits, and certifications at each stage. The original intention of caring for the environment will continuously evolve through the interplay of ideals and reality. The key to maintaining the ideal of a green factory is to adhere to the principle of minimizing environmental impact and making solid progress step by step.
Green Building
What Is Green Building?
Green buildings have different names and definitions in each country. The earliest concept of green building was in the 1960s, which was about the low environmental impact represented by "environmental symbiosis housing" from Japan and the "ecological building" from the United States. Until 1990, the United Kingdom issued the world's first standard of green building. The purpose was to implement the norm of "use the least earth's resources and create the least waste" in the life cycle of a building, from renovation, planning, construction, and operation to demolition. Each country will create its green building standards according to its geographical and climatic conditions.
The Green Building Certification System
In 1999, the Taiwanese government established the Green Building Certification System, known as EEWH, which came right after the LEED in the US. The EEWH includes four main aspects - Ecology, energy saving, waste reduction, and health. The green building works for all the project types, which have four options: basic, residential, Eco-community, industrial, and building renovation.
The Green Building Regulations and Enforcement Rules
According to the Green Building Assessment Manual – the green building assessment has been divided into nine categories.
Ecology
Ecology can be evaluated in three aspects -
|
1. |
Biodiversity: This assesses the area of biological habitats and activities in natural areas such as vegetation, soils, light pollution, and biological movement barriers. This metric only applies to the project if more than one hectare. |
| 2. | The level of the greenery: The difference between this index and the ecological diversity index is in quantity and quality. The amount of greening is calculated according to the type of planting, and the soil depth is required to be 0.3~3.5m. Floristics can be divided into ecological multistratal, arbor, shrubs, perennial vines, flowerbeds, meadows and old trees, etc. |
| 3. | Soil moisture conservation: It refers to water content capability, as well as the storage and infiltration of rainwater. The higher the water retention, the better to help the microbial activity in the soil. It can improve the organic quality of soil and cultivate plants. The water retention can be calculated through the area of green space and the volume of garden soil, the paving area of permeable bricks, and other special water retention designs. |
Energy Saving
4. Energy saving can be evaluated in three following aspects-
A. The shell of the building: The building design should include ventilation, and roof insulation of heat to avoid the need for air-conditioning. Using energy-saving glass can help to reduce indoor temperature, etc.
B. Air-conditioning: High-efficiency air-conditioning system, energy-saving, CO2 detection, etc.
C. Lighting: To maintain daylight, all indoors should have sufficient windows. By using energy-saving lamps with automatic dimming, a control system, and chosen high-brightness colors to improve the lighting level, etc.
Waste Reduction
5. CO2 reduction: It is to review the CO2 content that includes bricks, tiles, rebar, and glass in buildings. CO2 emissions will be scored based on 4 structures: structure rationalization, lightweight construction, durability, and recycled materials. For example, the building should be as regular and square as possible; the use light rebar and the use of lightweight material for partition walls. Additionally, seismic resistance and the use of recycled materials should also be considered.
6. Waste reduction: It is aimed at comprehensive pollution control in the process of building construction. Among them, construction pollution sources include construction waste, solid waste from demolition waste, engineering balance earthwork, and construction air pollution. Suggested solutions include installing dust-proof nets, and dust-proof plastic cloths, setting up wastewater pollution treatment systems and using recycled building materials.
Health
7. Indoor environment: This index appeals to low pollution, low fugitive, and recyclable building materials design to evaluate whether it is friendly to human health and the global environment. This can reduce the harm of carcinogens to the human body and the burden on the earth. The indoor environment is divided into four categories: light environment, sound environment, ventilation, and indoor building materials.
8. Water resources: According to the geographical environment and climatic conditions of Taiwan, take the advantage of more than 2,500 mm of rainfall annually that makes good use of water resources. Recycling water resources can help to reduce the cost of development and to avoid the loss of water. Water resources assessment such as products with water-saving labels-faucets, toilets, public hydrants; planning rainwater recovery systems to calculate water storage levels, etc.
9. Improvement of sewage and garbage: Mainly to evaluate whether the sewage and garbage treatment system is implemented and should be strengthened. For example, all domestic miscellaneous water discharge systems should be connected to sewage pipes and treatment facilities, sufficient space for garbage placement and transportation, geotechnical installations for recycling, food waste collection systems, etc.
The Green Building Rating System
According to the green building assessment, the score range has been divided into:
- Diamond
- Gold
- Silver
- Bronze
- Passed

How Did We Design the Green Building?
Layana was certified with Gold-level Green Building (EEWH-Gold) in 2018, in Taiwan. The essence is a manufacturing factory, so the application category is a green building factory. In the early stage of plant planning, it developed along the four principles of energy saving, greening, health, and waste reduction. Among them are the targets for significant improvement:
- The level of the greenery – through gardens, planting, green space, etc., the total green area is 4,780 square meters, and the greening ratio is 37.8%
- Soil Moisture Conservation – using water permeable pavement, the area, and the volume of the gardening area to calculate the water retention. ZQi=328.37
- Energy saving from the shell of the architecture – widely added windowsills to avoid direct sunlight, plus inlaid the heat insulation materials into the rooftop, can reduce the heat transfer rate. Layana’s headquarter is on average rate.
- Energy-efficient air conditioning – chose the right air conditioning system which includes air purification, and energy recovery ventilation (ERV) to comply with the rules of energy saving.
- Water Saving – Layana’s headquarter used a raft foundation to create the rainwater recycling system. Rainwater is stored in the basement which can save 7,900 tons of water every year. Please find the further story here.
- CO2 reduction – Layana executes recycling, regular cleaning, and minimizing the waste of construction can dwindle the carbon emission.
The Benefits of the Green Building
- Energy Saving – first of all, the construction cost may be higher than the average cost of a building project. However, in the long term, the energy cost can be saved a lot by complying with the regulations of green buildings.
- Low Maintenance Cost – if the architecture planning is well considered before the construction start, then its following maintenance for green buildings can be easier than for non-green buildings. For example,
- Raised the quality of the working environment – creating a healthy, comfortable, and sustainable indoor environment can improve human beings in both physical and mental ways. CO2 detectors can monitor indoor CO2 density.
The Effects of Having Green Buildings
It changed the values of the land and properties. For example, in Taiwan, according to the level of green building, the living area, and the original property price, there is a green premium between green buildings and non-green buildings, and it will last over time. (2017) In short word, green buildings can raise the value of the property itself, and non-green-buildings decrease at the same time.
The Guidelines for Green Building Projects
- Understand the types of green building projects – to know the project direction whether is new building construction or an existing building renovation, then to see which category suits the best - residential, commercial/industrial, eco-community, or building renovation.
- Set up a target of Green Building Certification – according to the rating system, it would suggest that design a building architecture in according to the nine categories of green building. If the project is a renovation, then an analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of achieving green building certification is a need. Making the most efforts in the right place will be the effective way to acquire the certificate.
- Create a task force – the team should be multidisciplinary, which includes quality, accounting, facility management, and procurement to go through the project. The team should be competent and actively involved in the process.
- Find the right person – the architect shares the same values with the owner and is willing to make the project happen.
- Choose suppliers wisely and carefully – suppliers include contractors and hardware systems. It would be beneficial to understand the capability of contractors if the project manager can visit some physical examples of contractors.
- Monitor the quality of the construction continuously – to maintain the quality of the structure, the task force can help to validate materials, generators, air conditioning, and so on. External audits are required during the construction period.
- Execute the acceptance of work – the quality of the construction should be consistent throughout the project. Every phase should have inspections or acceptance of work to get approvals from external audits.
- Execute the contract – as a project leader, an incentive can encourage constructors to finish the work before the deadline with the same quality. If constructors need to prepay expenses, then allow it within capable range.
- Execute the facility test – use the actions to validate the finished work. For example, the production can produce a batch of products successfully.
The Summary
The definition of green architecture nowadays extends beyond just the appearance of buildings; it also encompasses the importance of sustainable design in terms of building materials and construction methods. These practices all aim to reduce environmental impact and achieve the goals of "environmental prosperity" and "health and wellbeing" through energy-efficient, low-carbon, and sustainable operational approaches. The current development of green architecture in Taiwan has achieved some success, and in addition to green building certification, there are other sustainable initiatives that can be implemented, such as energy management systems and sustainable manufacturing in factories. For this precious planet, businesses should continuously strive to protect and conserve, without ceasing.
Cleaner Production
What Is the Cleaner Production?
Recently, the urgent need to reduce the industry's carbon footprint led to the term cleaner production being on everyone's lips today. However, only a few companies integrate a comprehensive strategy to achieve cleaner production. Cleaner production refers to new procedures and technological solutions enabling new practices at all industrial production levels for environmentally sustainable manufacturing. Reducing or eliminating potentially harmful components, minimizing the emission of waste of any kind to the environment, and achieving the product by reducing the amount of energy, hydrological resources, or the needed input materials, will contribute to cleaner production within an environmentally sustainable company.
The Characteristics of the Cleaner Production
- Renew Equipment – Installing more efficient equipment to use a smaller amount of material or inputs and require less electricity, water, or other resource consumption.
- Improvements in the usage of material – Implement improvements or new technologies to take more advantage of the available materials, avoid waste, or replace polluting materials.
- Design innovation – Reduce the amount of material needed or design more durable products over time.
- Improvements in waste treatment – Reuse and recycle all excess material and treat, reduce, and even eliminate waste before released into the environment.
- The Substitution of Packaging and Labeling – Decrease the amount of plastic and use materials that are recycled or obtained from cleaner production.
- Source materials locally – Use inputs from local manufacturers and optimize the distribution chain by reducing the mileage needed for inputs to reach the factory and for manufactured products to reach the end customer.
- Improvements in production and maintenance tasks – Prevent future potential environmental damage.
Improvements in facilities – Protect the health of employees and reduce energy, water, or any other resource consumption.
Cleaner production is a comprehensive concept that integrates all company departments. For the correct implementation of a strategy for cleaner production, it is necessary to coordinate and involve all the teams and all the departments to find possible failures, inefficiencies, or opportunities, propose and analyze potential improvements, and implement and measure them. Furthermore, when designing the corporative policy regarding environmental sustainability, it is critical to emphasize the continued implementation of cleaner production plans. Continuous improvement is how a business can stay competitive.
The Benefits of the Cleaner Production
The benefits of applying a cleaner production program are multiple and can be classified into two groups: social & environmental benefits and corporate benefits.
On the one hand, as mentioned in previous lines, companies continuously implementing an improvement program to achieve cleaner production proactively contribute to the collective achievement of a large part of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs' sustainable development goals. Through the implementation of cleaner production, we can contribute to the following achievements (UN official goal numbering in brackets):
- Good health and well-being (3) – A cleaner production site will be a much more pleasant and healthy environment (both physically and mentally) for employees. We can better prevent accidents at work, ensure that workers are healthy, and thus help relieve public health services.
- Clean water and sanitation (6) – Rainwater collection systems will help reduce water consumption, reducing demand and increasing clean water availability for those in need. Besides, for industrial water purification systems, a decent water purification and drainage system will ensure that the water after its industrial use can be recycled and reused.
- Affordable and clean energy (7) – By improving the energy efficiency of production equipment, the industrial demand for energy decreases, which will contribute to an energy price drop for households. In addition, increasing the demand for clean energy by incorporating it into industrial uses will boost renewable energy development, improving its technology and competitiveness.
- Decent work and economic growth (8) – Implementing a cleaner production program will help to improve the local business fabric resilience, preparing companies to be more competitive in the future and generating higher quality employment.
- Industry, innovation, and infrastructure (9) – The success of a cleaner production program is due in part to technological solutions or innovations in processes that make it possible to achieve more efficient use of available resources or reduce waste. The continuous search for these solutions will contribute to the development of collective ingenuity and the workers' preparation.
- Sustainable cities and communities (11) – A cleaner production is an inevitable step in turning a traditional factory into a green factory. Green factories help to create more sustainable, safe, and resilient cities.
- Responsible consumption and production (12) – Cleaner production is closely related to eco-efficiency since one of the ultimate goals is to reduce the carbon footprint when producing new goods. It is necessary to know how to convey to the customer the benefits of a cleaner production system so as not only to promote responsible production but also responsible consumption.
- Climate action (13), life below water (14) and life on land (15) – According to the European Environment Agency, industrial processes account for 9.1% of total greenhouse gas emissions, without counting the emissions emitted by the generation of energy necessary to feed factories. It is vitally important to reduce the carbon footprint when producing goods because the environmental consequences of rising temperatures can seriously jeopardize the fragile balance of ecosystems needed for the proper development of human and animal life. Melting ice from the polar caps, floods, droughts, devastating storms, or plagues are just some of the terrible consequences if the earth's average temperature keeps rising.

On the other hand, at a corporate level, the implementation of a cleaner production system has numerous advantages:
- Energy savings – Even though sometimes the installation of more energy-efficient equipment means higher installation or implementation costs, it will save on electricity bills in the long run.
- Water saving – Using water recycling systems means significant annual savings in water bills, apart from making the company more resilient to potential supply problems.
- Increase employees' efficiency – A clean environment, with clean air and adapted room temperature, stabilize employees’ health and work efficiency. In addition, many of the plans included in cleaner production programs bring measures that reduce the possibility of accidents at work.
- Improved company image – A company will have a better reputation and more prestige when it is concerned with reducing its carbon footprint and cares about taking care of its employees and members of the community where the company is based. It is also synonymous with transparency and commitment.
- Improved profit margins – Making better use of the material at the production time and reducing the amount of waste processed before emitting it into the environment will increase profit margins.
The Obstacles to the Implementation of the Cleaner Production
Although cleaner production systems bring numerous benefits overall, there are also concerns that lead some businesses to not prioritize clean production plans and instead postpone their implementation until national regulations compel them to make improvements. Some of these concerns include:
- Lack of funding for improvements - Implementing improvements sometimes requires a financial investment. In such cases, the motivation for investment and the potential long-term benefits of the improvements need to be carefully considered.
- Lack of cohesion - Implementing a clean production plan requires the full participation of all departments. It can be challenging to coordinate tasks and communicate effectively across different departments during the process.
- Lack of technological resources - Not all company departments can apply clean production system solutions at the same pace. However, companies should approach clean production with the same determination and commitment.
- Lack of environmental awareness - Not all companies consider environmental conservation as a core value and a guiding objective. Layana, on the other hand, not only recognizes sustainable development as an imperative goal but also believes that continuous improvement will consistently reduce carbon footprint and protect the environment.
The Exampple of Implementing the Cleaner Production
For instance, Layana's implementation of cleaner production encompasses a series of plans and measures categorized into three main areas: production and manufacturing, environmental design, and green management and social responsibility. These three categories not only harness the collective efforts of various departments but also demonstrate innovation in seeking solutions, which serves as the fourth criterion for evaluation. As a result, in 2022, Layana was awarded the Clean Production System Assessment Certificate. This certification validates the company's commitment to enhancing ecological efficiency and product yield while diligently reducing waste and minimizing adverse impacts on the environment and human health.
(1) Production and Manufacturing
This plan consolidates all the improvement measures implemented at Layana to reduce energy consumption, lower production costs, and enhance the working environment. Within these improvement measures, the following projects are included:
Energy Saving
- Implementation of automated warehousing: This measure reduces energy consumption and the emission of gases and other pollutants (as we require fewer warehouse equipment and space). Furthermore, compared to traditional warehouses, the installation of automated warehousing alleviates physical burdens on employees and reduces the probability of industrial safety accidents.
- Installation of LED lighting throughout the entire factory: Replacing traditional light tubes with energy-efficient LED lights not only contributes to energy savings but also enhances illumination.
- Deployment of heat recovery systems: By installing insulation materials in various factory equipment and heat recovery systems, we reduce energy consumption and maintain a conducive temperature within the factory.
- Adoption of alternative molds for material conservation: Through the use of substitute molds, our technical team significantly reduces material waste and manufacturing costs.
Investment in variable frequency air compressors: By phasing out fixed-frequency air compressors and adopting variable frequency ones, we greatly contribute to substantial electricity savings and reduced energy consumption.
Water Conservation
This program comprises two primary objectives: the reduction of water loss and the establishment of a system for rainwater collection.
- By installing sediment cooling towers to replace traditional water towers, we can minimize water loss (evaporation and splashing losses) and decrease water and energy consumption as well as production costs.
- The implementation of a rainwater harvesting system facilitates significant water conservation. Additionally, it equips Layana with the capability to respond to natural disasters, ensuring acute water shortages can be alleviated in the event of water supply issues such as droughts or malfunctions.
(2) Environmental Design
Environmental design refers to the innovative approach of focusing on the impacts on human health, chemicals, and the environment and economy during the design and manufacturing of commercial products and processes, rather than being solely driven by regulatory inducements. For example, all the improvement measures implemented at Layana serve not only to enhance products but also to improve employees' working conditions and the environment, while contributing to environmental protection:
- Reduction of plastic usage: Substituting plastic materials used in product packaging with alternatives such as recyclable paper and biodegradable materials.
- Incorporation of carbon footprint labels in Naya's products: Examining the carbon emissions from raw material production to the manufacturing and transportation processes, providing transparency for consumers to choose low-carbon products.
(3) Green Management and Social Responsibility
- Layana engages in various sustainable activities across different domains to contribute to the welfare of society, employees, and surrounding communities. Regular seminars on public welfare and environmental protection are organized by Layana. Furthermore, through the sponsorship of films screened at the 4K3D Dolby Cinema, we promote environmental awareness and highlight the impact of climate change on the natural environment, advocating for a low-carbon/low-energy lifestyle.
- Layana also believes in creating a green working environment to enhance employee health and safety, and encourages a green movement where everyone contributes to environmental conservation. Within the factory, Layana's colleagues utilize eco-friendly utensils, practice paperless office operations, and continuously recycle stationery materials.
Taiwan's Cleaner Production Assessment System
In alignment with the international environmental trends, the Taiwanese government encourages energy conservation and carbon reduction in our country's industries. In 2012, they established the Green Factory Labeling System. The qualification for the Green Factory Label requires compliance with both hardware and software aspects of green specifications. On the hardware side, the factory buildings must obtain the Ministry of the Interior's Green Building Label. On the software side, production and operational management must pass the Industrial Development Bureau's Clean Production Assessment. The Clean Production Assessment System is one of the qualifications for the Green Factory Label, and it is divided into the "General Industry Clean Production Assessment System" and the "Specific Industry Clean Production Assessment System."
Layana's factory falls under the category of the General Industry Clean Production Assessment System, and it successfully passed the Clean Production Assessment System in 2022.
Summary
The implementation of cleaner production enables factories to meticulously scrutinize the possibilities of waste reduction, recycling feasibility, and opportunities for energy conservation and carbon emission reduction within the working environment. This not only allows enterprises to minimize their environmental impact during the manufacturing process but also empowers each individual engaged in cleaner production to contribute to tangible, environmentally conscious actions.
Since 2016, through the collective efforts of all departments and employees at Layana, we have steadily achieved significant milestones in the Green Building and obtained the Clean Production System Assessment, making us the pioneering green factory in Changhua County. By embracing cleaner production, Layana has transformed itself into a more comprehensive and environmentally sustainable enterprise, encompassing aspects ranging from building structures to implementing office stationery recycling. Moving forward, we shall further endeavor to reduce our carbon footprint in accordance with current manufacturing emissions. After all, there can never be too many benevolent actions that humanity can undertake for the betterment of the environment.