| Sample Product | Plastic pedal | |
| Industry | Agriculture | |
|
Application |
Farm Equipment | |
| Materials | Nylon |
|
|
Plastic pedals are becoming essential in a variety of industries, from automotive to medical and industrial applications. Their unique combination of lightweight design, durability, and cost-effectiveness makes them a preferred choice over traditional metal pedals. Resistant to corrosion and easier to manufacture, plastic pedals meet the demands of modern manufacturers looking for innovative, reliable, and high-performance solutions.
|
Layana: Your Trusted Plastic Pedals Manufacturer
With decades of experience in plastic injection molding, Layana specializes in manufacturing high-quality plastic pedals and injection molds. We are a Taiwan-based, IATF 16949-certified company proudly working with some of the world’s top automotive OEMs. Layana supplies plastic pedals for various applications, including passenger cars, trucks, off-road vehicles, and industrial equipment.
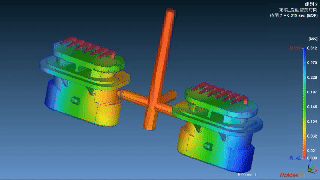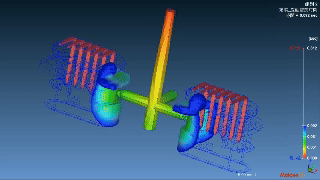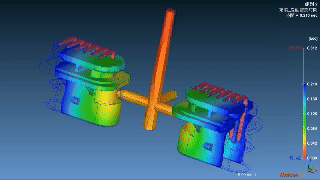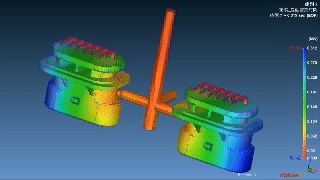 |
| Item/Type | Vertical Injection Machinery | Horizontal Injection Machinery |
|---|---|---|
| Tonnage Range | From 35T to 250T | From 60T to 200T |
|
Maximum Product Size |
INCH: 8.5 x 11 x 6 MILLMETER: 216 x 279 x 150 |
|
|
Maximum Product Weight |
0.1g~500g | |
| Preciseness |
Mold: ± 0.005mm Product: ± 0.03~0.05mm |
|
We are dedicated to producing safety-critical plastic pedal components that meet the highest standards of quality and reliability.
From material selection to mold design and production, every stage we handle with precision and care.
|
Design for Manufacture (DFM)
Utilizing advanced mold flow analysis software, we meticulously assess critical aspects such as flow balance, hub analysis, and venting line design. |
Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA) PFMEA includes stringent material control through rigorous inspections and meticulous equipment management to ensure optimal performance. |
Surface Texture
Whether you require intricate engraving based on your specifications or alternative texture patterns for validation, we deliver exceptional results. |
Plastic Pedal Manufacturing Process
- Design and Simulation: Precision molds are designed using advanced software to optimize part geometry and material flow.
- Material Selection: High-performance plastics like nylon, ABS, and polypropylene are selected based on project requirements.
- Injection Molding: Molten plastic is injected into molds under high pressure to form the pedal’s shape.
- Cooling and Finishing: Components are cooled, trimmed, and inspected to meet quality standards.
Common Materials of Plastic Pedals
- Polyamide (Nylon): Offers high strength, flexibility, and excellent wear resistance.
- Polypropylene (PP): Known for chemical resistance and fatigue resistance.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Provides strength, toughness, and a good surface finish.
- Polycarbonate (PC): High impact resistance and dimensional stability.
- Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE): Combines the properties of rubber with the recyclability of thermoplastics for improved grip and comfort.
To enhance material properties, plastics can be reinforced with additives:
- Glass Fibers: Increase tensile strength and stiffness.
- Carbon Fibers: Offer high strength-to-weight ratios and improved fatigue resistance.
- Aramid Fibers: Provide excellent impact resistance and toughness.
- Mineral Fillers: Improve dimensional stability and reduce shrinkage.
The Applications of Plastic Pedals
Automotive Industry
Plastic pedals have revolutionized vehicle design, replacing traditional metal pedals with a lightweight, corrosion-resistant alternative.
- Accelerator Pedals: Designed for electronic throttle control (drive-by-wire) systems, these pedals are lightweight and integrate advanced sensors for precise control.
- Brake Pedals: Manufactured with high-strength materials to withstand intense stress during braking, while absorbing vibrations for a smoother driving experience.
- Clutch Pedals: Ergonomically designed for manual transmission vehicles, providing enhanced comfort and reducing driver fatigue.
|
Semi Truck Pedals |
Agriculture Vehicle Pedals |
Off-Road Vehicle Pedals |
Commercial Vehicle Pedals |
Utility Vehicle Pedals |
-
Industrial: Plastic pedals are utilized in equipment and machinery where durability, precision, and safety are the top priority.
-
Machine Controls: Plastic pedals serve as reliable machine controls in assembly lines, packaging machines, and robotic systems. They offer consistent performance with reduced maintenance needs, essential for minimizing downtime in industrial operations.
The Advantages in Industrial Applications
- Corrosion Resistance: Ideal for harsh industrial environments where exposure to chemicals and moisture is common.
- Electrical Insulation: Enhances safety when operating electrically powered machinery by preventing electrical conductivity.
- Customizable Design: Tailored to specific operational needs, including pedal size, shape, and resistance.
- Durability: Engineered to withstand heavy usage and mechanical stress.
Medical Equipment and Others
- Surgical Devices: Plastic pedals in surgical equipment allow for hands-free operation, maintaining sterility during procedures. They enable surgeons to control devices such as electric scalpels, laser instruments, and imaging equipment without compromising the sterile field.
- Dental Equipment: Dentists utilize plastic pedals to operate tools like dental drills and suction devices, keeping their hands free to focus on patient care. The pedals are designed for precise control and ergonomic comfort during long procedures.
Beyond medical equipment, plastic pedals are found in:
- Musical Instruments: Foot pedals for guitars, keyboards, and electronic effects.
- Bicycles: Durable and lightweight pedals for various cycling disciplines.
- Consumer Electronics: Foot controls for gaming, sewing machines, and fitness equipment.
The Disadvantages of Plastic Pedals
Mechanical Strength Limitations
- Load-Bearing Capacity: This may not be suitable for extremely high-stress applications without reinforcement.
- Wear and Tear: Potential for faster degradation under heavy use compared to metals.
UV Degradation
- Structural Integrity: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light can degrade some plastics, affecting performance. These may require UV-resistant additives or coatings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Does Layana commercialize pedals?
2. How can Layana help manufacture pedals?
3. What is the difference between safety parts and standard parts?
| Aspect | Safety Parts | Normal Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Strict industry standards, third-party certification, full traceability | General industry standards or internal guidelines |
| Inspection Frequency | Multiple stages, increased frequency, continuous monitoring (SPC) | Inspections at key points, random sampling |
| Testing Methods | Advanced tests (crash, fatigue, destructive testing) | Basic dimensional checks, functional and visual inspection |
| Documentation and Traceability | Detailed records, full traceability | Less detailed documentation |
| Failure Tolerance | Zero-defect tolerance | Minor cosmetic or non-critical defects may be allowed |
| Supplier and Process Audits | Strict audits, regular reassessments, full process control | Less frequent and comprehensive audits |
| Rework and Scrap Policies | Rework often not allowed; defective parts are scrapped | Rework allowed if defects are minor |
4. How many cycles can a plastic injection mold typically withstand, and what factors influence its lifespan?
5. What is the typical lead time for fabricating a plastic injection mold?
6. Are plastic pedals less reliable than metal pedals?