The Definition of In Mold Assembly
In‑mold assembly (IMA) is a multi‑shot injection molding process in which pre‑fabricated metal inserts—like terminals, busbars, or lead frames—are placed in the mold during the first injection (“pre-mold”). In the second (and any subsequent) shot, molten plastic flows around and fully encapsulate these inserts, locking them permanently in place within the part. By embedding conductive or structural elements directly into the plastic during the initial molding cycle, IMA eliminates all the time-consuming pick-and-place and manual fastening steps required in traditional post-molding assembly.
The Difference Between Typical Assembly and In Mold Assembly
|
Type/Item |
Typical Assembly |
In Mold Assembly (IMA) |
|---|---|---|
|
Process Flow |
Parts are produced individually, then joined in secondary process. |
Molding and assembly occur in one operation. |
|
Production Speed |
Lengthy secondary processes extend cycle times. |
Eliminates secondary steps, dramatically shortening cycle times. |
|
Accuracy |
Manual placement or separate‑assembly tolerances can introduce variation. |
Precise, repeatable component placement controlled directly within the mold. |
|
Component Strength |
Joints and adhesives can create weak points. |
Overmolding binds parts into a unified, durable structure with fewer potential failure sites. |
|
Cost Efficiency |
Higher labor costs, material waste (e.g. adhesives), and extra equipment needed. |
Fewer process steps reduce labor, cut material waste, and minimize reliance on additional equipment. |
The Process of In Mold Assembly
Overmolding is an advanced injection molding technique that uses two or more materials into a single, unified component—often embedding functional features such as terminals or busbars to boost structural strength and reliability. In mold assembly builds on this concept by placing prefabricated inserts—typically metal parts are directly inserted in the mold, eliminating all downstream pick‑and‑place and fastening steps. IMA proceeds in two stages, commonly called “first shot and second shot” or “pre-mold and overmolding,” each in its mold cavity:
- First shot (pre mold): Molten plastic is injected into the mold to form the base substrate. During this shot, you can place metal inserts such as terminals into the cavity. As the plastic cures, it locks these inserts firmly into position, creating a sophisticated, ready‑to‑augment framework.
- Second shot (overmolding): The pre-molded substrate is transferred into a second mold. A secondary material is injected around or over the existing structure. This shot can merge multiple pre-molded pieces into a single form and introduce new inserts (bushings, fasteners) for mechanical or sealing functions.
Depending on material choices and mold design, the two polymers bond through mechanical interlock or chemical adhesion. Once cooled, the result is a fully integrated part—complete with embedded metal elements—delivered from the mold, with no manual assembly steps required in traditional processes.
The Applications of In Mold Assembly
Automotive & EV In Mold Assembly: Modern vehicles demand components that are both lightweight and robust, with integrated electronics and power‑management functions. By embedding metal inserts—such as lead frames directly into structural parts (e.g., housings of EV charge ports, battery modules, power‑distribution units, and sensor assemblies), manufacturers create seamless electrical pathways without bulky wiring harnesses. This in‑mold integration simplifies assembly, cuts error rates, and delivers superior safety, reliability, and overall vehicle performance. Moreover, these components are engineered to pass stringent IPX environmental‑protection tests—such as IPX9—ensuring fully waterproof and dustproof performance for dependable operation in the harshest conditions. The products and the list below use automotive of an example how in mold assembly is applied in different functions.
|
Part/Product |
Embedded Inserts |
Reasons for In Mold Assembly Implementation | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
EV Charge Port (Inlet) |
High‑current busbars & terminals |
Low‑resistance power path; IP67 sealing; one‑step, leak‑proof assembly reduces defects & cost |
|
|
Engine Control Module (ECM) Housing |
|
Lead frames & connector terminals |
Accurate PCB alignment; integrated EMI shielding; robust environmental protection |
|
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor |
|
Diaphragm lead frame; heating‑element busbar; terminals |
Integrated deicing; exact sensor alignment; high‑pressure sealing |
|
Crankshaft Position Sensor and Camshaft Position Sensors |
|
Magnetic‑coil lead frame; snap‑in terminals |
Accurate coil positioning; direct plug‑in harness; eliminates manual insert work |
|
Transmission Control Module Housing |
|
Lead frames & overmolded connector |
Tight tolerance control; IP6K9K‑rated sealing; simplified assembly flow |
|
Knock Sensor |
|
Piezoelectric element lead frame; contact terminals |
High‑temperature stability; precise element placement; sealed against engine vibrations |
|
Ignition Coil Connector Housing |
|
Terminal inserts & lead frame |
High‑voltage insulation; precise spark‑plug interface; durable under‑hood sealing |
|
Fuel Pump Module |
|
Terminal block & busbar |
Fuel‑safe leak‑proof seal; integrated power routing; reduced part count |
|
Oil Temperature Sensor |
|
Thermistor lead frame; sealed terminals |
Durable high‑temp operation; integrated oil‑resistant seal; simplified assembly |
|
Taillight Assembly Connector |
|
LED busbar & terminal inserts |
One‑piece weatherproof housing; accurate LED placement; streamlined production |
|
Airbag Module Connector |
|
Terminal strips & lead frames |
Critical safety compliance; dust‑tight sealing; zero manual steps |
|
ABS/Wheel Speed Sensor |
|
Coil lead frames; sealed terminals |
IP6K9K‑rated sealing; precise coil placement; plug‑and‑play ECU connection |
|
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) |
|
Rotary‑encoder lead frame; multi‑pin terminals |
High‑accuracy angle feedback; direct ECU harness plug; robust environmental protection |
|
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor |
|
Hall‑effect lead frames; busbars; terminals |
Integrated multi‑signal distribution; high‑precision feedback; dust‑tight sealing |
|
Steering Angle & Torque Sensor |
|
Dual lead frames; pin terminal block |
Redundant signal paths; accurate torque/angle sensing; sealed housing for durability |
|
Rain/Light Sensor |
|
Photodiode lead frame; heating‑element busbar; terminals |
Integrated de‑icing; moisture protection; precise optical positioning |
|
Ultrasonic Parking Sensor |
|
Transducer lead frames; snap‑fit terminals |
Precise acoustic alignment; waterproof IP69K housing; direct harness connection |
|
Blind‑Spot Radar Module |
|
Power busbars; multi‑pin terminals; lead frames |
Integrated high‑power distribution; EMI control; one‑shot, rugged connector integration |
|
Airbag Crash Sensor |
|
Metal “sled” insert; electrical terminals |
Precise impact detection; sealed against contaminants; direct harness plug‑in |
|
NOₓ Sensor |
|
Ceramic sensing‑element lead frame; two‑pin terminal busbar |
Exhaust‑temperature resistance; integrated signal routing; leak‑proof housing |
Consumer & Electronics In mold Assembly: IoT modules, industrial sensor housings, LED‑lighting assemblies, medical‑monitoring devices, and power‑tool enclosures—the demand for compact, multifunctional designs is relentless. Embedding conductive elements such as busbars, lead frames, and terminals, directly into molded housings via in‑mold assembly lets engineers optimize PCB layouts, enhance thermal dissipation, and curb electromagnetic interference. This deep integration not only accelerates production and reduces material waste but also yields tougher, more reliable products perfectly suited to rugged industrial and advanced consumer‑tech applications.
The Benefits of In Mold Assembly
- Integrated electrical pathways: In mold assembly creates low resistance circuits with perfect alignment, eliminating secondary wiring and loose connectors.
- Built-in isolation: You can design molded insulation barriers around embedded inserts—busbars, connectors, and contact pins—to prevent short circuits and minimize electromagnetic interference in mixed‑signal environments.
- Save material: Integrating metal parts or micro‑connectors directly into the plastic frees up board space and sheds extra wiring bulk—critical for automotive, aerospace, and compact industrial electronics.
- Optimize thermal management: Embedded metal elements can be positioned to form heat‑dissipation pathways, channeling heat away from sensitive components and improving cooling in power modules and LED‑lighting assemblies.
- Lowered cost: In mold assembly has fewer discrete parts (no separate wiring harnesses or housings) combined with fewer assembly stages to drive down material and processing expenses—making your design more competitive.
- Enhanced durability: In mold assembly encases busbars, lead frames, terminals, and connectors in a protective polymer skin, shielding them from vibration, moisture, and environmental stress for longer service life.
Layana’s In Mold Assembly Capabilities
We refined our manufacturing expertise by combining overmolding with insert molding with precision progressive die stamping, all performed in-house. We create robust, high-performance assemblies tailored for variable applications.
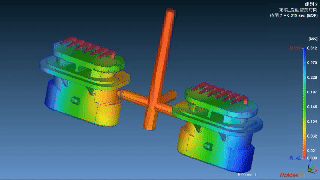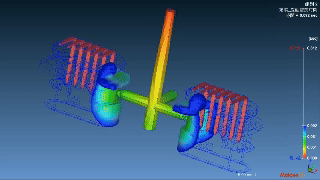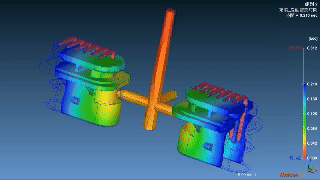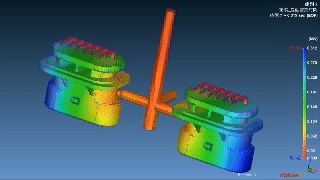 |
| Item/Type | Vertical Injection Machinery | Horizontal Injection Machinery |
|---|---|---|
| Tonnage Range | From 35T to 250T | From 60T to 200T |
|
Maximum Product Size |
INCH: 8.5 x 11 x 6 MILLMETER: 216 x 279 x 150 |
|
|
Maximum Product Weight |
0.1g~500g | |
| Preciseness |
Mold: ± 0.005mm Product: ± 0.03~0.05mm |
|
|
The Bi-material Integration at Layana brings several key advantages
|
Conclusion
In today’s fiercely competitive manufacturing landscape, companies are constantly seeking ways to boost efficiency and enhance product quality. In mold assembly has emerged as a game‑changing technique, replacing traditional step‑by‑step processes with a single, integrated operation inside the mold. Layana Company stands out as one of the industry’s leading specialists in in‑mold assembly, the integration of plastic injection and metal stamping and its full suite of in‑house capabilities—from industrial automation to mold design and fabrication—all under one roof. This end‑to‑end approach enables Layana to respond with remarkable speed and precision, delivering cutting‑edge in‑mold solutions—especially for complex lead frame pre‑mold and overmolding designs in power electronics and next‑gen EV applications.