The Definition of Plastic Injection Molding
The plastic injection molding technology is widely used in the production of various plastic products required for daily life. Plastic injection molding is a process of melting granular plastic raw materials into a flowable state at high temperature and high pressure, injecting the melted plastic raw materials into the mold under high pressure, waiting for a period of time to cool, and then using a top pin to remove the plastic product from the mold to obtain various plastic products.
What are the materials utilized in plastic injection molding? What are the products that use them?
| Code | Heat Resistance | Impact Resistance | Abrasion Resistance | Toughness | Glossiness | Chemical Resistance | Transparency | Stability | Electrical Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | 90°C | ▲ | ▲ | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | Widely used in automotive interiors, containers, toys, and electrical enclosures. | |||
| High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) | 70°C | ♢ | ▲ | ▲ | ▲ | Widely used in audio and clock housings, and electronic products. | ||||
| Acrylonitrile-Styrene (AS) | 80°C | ▲ | ♢ | ♢ | Widely used in electric fan blades, battery casings, humidifier casings, and more. | |||||
| Benzene Butadiene Styrene (BBS) | 85°C | ♢ | ▲ | ▲ | ♢ | Widely used in telephones, computer terminals, household appliance casings, and more. | ||||
| Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) | 80°C | ▲ | ♢ | ♢ | Widely used in lighting fixtures, bathroom equipment, office stationery, and more. | |||||
| Polyoxymethylene (POM) | 130°C | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | Widely used in switches, gears, washing machines, automotive parts, household appliances, and more. | ||
| PC | 130°C | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | Widely utilized in the application of protective mirrors, dashboards, hair dryers, lighting equipment, and electrical components. | |||
| PA | 160°C | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | ▲ | ♢ | ♢ | Widely utilized in the application of mechanical parts (slides, zippers), automotive parts, and fan blades. | ||
| PBT | 205°C | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | ▲ | ♢ | ♢ | Widely utilized in the application of electronic motor parts (sensors, switches), automotive parts. | ||
| PPS | 260°C | ▲ | ♢ | ♢ | ▲ | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | Widely utilized in the application of automobiles (valves, electronic control parts), plastics, and connectors. | |
| PET | 250°C | ♢ | ▲ | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | Widely utilized in the application of lighting fixtures and electrical components such as fan blades and capacitor boxes. | |
| PU | 100°C | ♢ | ♢ | ♢ | ▲ | ♢ | ▲ | ♢ | Widely utilized in the application of electronic switch handles, toys, suction cups, and automotive parts. | |
| PC+ABS | 120°C | ▲ | ♢ | ♢ | ▲ | ▲ | ♢ | ♢ | Widely utilized in the application of rolling door casings, motor part casings, and automotive parts. | |
| PA 6 | 295°C | Widely utilized in the application of electronic components in SMT technology. | ||||||||
| PA 46 | 270°C | Widely utilized in the application of electronic switches and insulating materials. |
What are the steps in the plastic injection process?
The five actions in the cycle of plastic injection molding are: plasticization, injection, holding pressure, cooling, and demolding.
- Plasticization: The plastic material is melted in the barrel using high temperature and high pressure. Based on the selected plastic material's characteristics, the processing temperature of the plastic material is set on the machine to ensure proper melting.
- Injection: After the plastic material is melted in the barrel, it is injected into the mold through the nozzle by the rotating screw. The internal space of the mold is used to shape the plastic material. It is important to adjust various parameters according to the conditions of plastic injection molding or the condition of the mold to avoid issues such as dimensional inaccuracies and flash during subsequent molding.
- Holding Pressure: When the material is injected into the mold and is cooling and shrinking, but the gate has not solidified yet, plastic is continuously injected to fill the space caused by cooling shrinkage until the gate solidifies. This helps reduce or prevent sink marks.
- Cooling: The molded product remains in the mold for solidification and cooling. Cooling time accounts for approximately 75% of the entire production process.
- Demolding: After the mold opens, the molded product is removed from the mold using ejector pins on the mold.
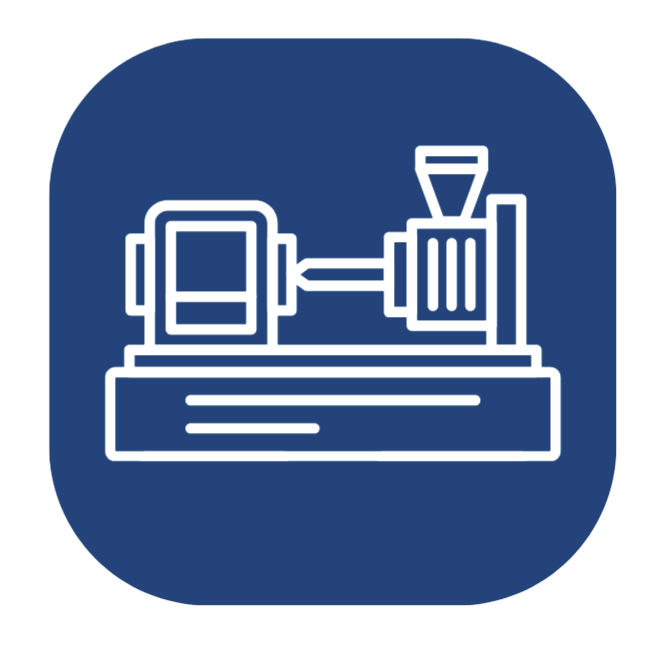
The plasticization structure of a plastic injection machine:
- Drying Hopper: It is used to pre-dry and store plastic raw materials.
- Barrel: It is a passage through which plastic raw materials flow to the mold.
- Screw: The barrel is equipped with a screw, which melts plastic pellets through high temperature and high pressure. The screw, through rotational movement, injects a precise amount of plastic through the nozzle into the mold.
- Mold: It is used to inject the material into a specific shape and mold the product accordingly.
- Ejector Pin: The ejector pin is a part of the mold and its main function is to push the molded product out of the mold, separating it from the mold.
Layana's Plastic Injection Molding Capabilities
Layana has introduced a dual alloy barrel system, making plastic injection molding production smoother. From precision injection molds, continuous stamping molds, mold subcontracting, injection molding, stamping parts processing to product assembly, we provide customers with the highest quality services. Plastic injection molded parts are suitable for medical devices, automotive precision parts, electronic components, connector parts, sensor system parts, and more.
 |
| Item/Type | Vertical Injection Machinery | Horizontal Injection Machinery |
|---|---|---|
| Tonnage Range | From 35T to 250T | From 60T to 200T |
|
Maximum Product Size |
INCH: 8.5 x 11 x 6 MILLMETER: 216 x 279 x 150 |
|
|
Maximum Product Weight |
0.1g~500g | |
| Preciseness |
Mold: ± 0.005mm Product: ± 0.03~0.05mm |
|
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Plastic Injection
Advantages
- High-quality products can be produced with minimal finishing processes.
- Plastic raw materials are inexpensive, allowing for low-cost production.
- Injection molding has high production efficiency, making it suitable for large-scale production with good quality.
- Through different injection molding techniques, different materials can be simultaneously molded, such as multi-material injection molding, co-injection molding, and encapsulation molding.
- Through mold design, complex structural molded products can be produced while also meeting the functional requirements of product appearance design.
Disadvantages
- Although plastic raw materials are inexpensive, the cost of molds is high.
- More technical manpower is required for processing and modification.
- The more precise the product structure, the more processes are required in mold design and manufacturing.
- Not suitable for small-scale production due to high mold costs and the purpose of reuse in repetitive manufacturing.
The Considerations for Plastic Injection Molding
In the process of plastic injection molding, the technical proficiency of personnel is of paramount importance. The so-called technical proficiency refers to the control of injection parameters, with adjustments made as necessary. We categorize the adjustment range of plastic injection parameters into five main classes: "temperature", "pressure", "velocity", "position", and "time". Among these, temperature holds particular significance as it is used to regulate the drying temperature of plastic raw materials, the heating temperature of the injection machine barrel, and the cooling temperature of the mold. Other parameter settings are adjusted according to the steps of plastic injection and the injection conditions of each product, with fine-tuning done at appropriate times. In the early days, artisans relied more on intuition or experience when operating the machine, but with advancements in technology, modern injection molding machines can now make parameter adjustments based on real-time data feedback.
Summary
Plastic injection is a rapid manufacturing method for producing plastic products. However, there are many factors that need to be carefully considered and attended to during the process, such as cost, selection of injection machine models, material selection, and mold manufacturing. A comprehensive evaluation from various aspects is required.