What Is Microstamping?
Micro Stamped Parts by Layana
Microstamping (microstamping), also known as precision stamping, micro precision stamping, miniature stamping, or micro forming, refers to the production of miniature parts characterized by micro features. This microstamping process is a specialized form of metal stamping that operates on a microscale, with down-sized operations. Unlike traditional metal stamping that typically handles larger components, microstamping is designed to work with delicate, microscopic-scale materials, creating parts measured in millimeters or even micrometers.
The Types of Microstamping Dies
Microstamping dies are classified into three main categories: single dies, progressive dies/compound dies, and fine blanking dies.
- Single Dies:
Single dies are designed to perform only one specific operation and are divided into the following subcategories. - Micro Punching Dies:
These dies, also called micro piercing dies, are used to create precise holes in metal sheets or strips. - Micro Blanking Dies:
These dies perform micro-blanking operations (cut out specific shapes or profiles from metal sheets or strips). - Micro Forming Dies:
These dies are used for the precision forming of micro parts utilizing techniques such as micro bending (also called micro-bending) and micro drawing (micro-drawing), or even micro deep drawing operations (micro cupping). - Other Dies:
Other microstamping simple dies to perform more specific operations. - Micro Progressive Die and Micro Compound Die:
Progressive dies and compound dies (or combination dies) are designed to perform multiple operations within a single die, making this approach more cost-effective than single-operation dies. Progressive dies are a type of tooling used for high-complex stamping, where a material strip is fed into a stamping press and continuously moved through various stations within the tool. - Micro Fine Blanking:
Fine blanking is a high-precision part stamping technique that accurately performs blanking to eliminate the secondary process by forming a smooth cut. Due to the small size of the miniature components, the fine blanking technique can be a great solution to avoid problems during secondary processing because of the material handling or the high cost of the precision equipment required for processing such tiny parts.
Layana’s Capability of Customized Microstamping
Having assembled a professional R&D team with decades of microstamping experience and expertise, Layana manufactures various complex micro parts smaller than 10mm with ±0.01mm accuracy, leveraging our cladding capability and metallurgical knowledge. We specialize in micro-precision stamping of miniature metal stampings.
Layana has a core team of toolmakers, some with 40 years of experience from simple dies to progressive dies, and toolings are mostly made in-house.
|
Category |
Capability |
|---|---|
|
The Maximum Size of a Tooling |
Up to 2,500mm*1,000mm*550mm |
| The Maximum Weight of a Tooling | Up to 1,200kg |
|
Range of Material Thickness |
0.02mm~6mm |
|
Tolerance Range |
Up to ±0.01mm |
|
Productivity/Month |
10 sets of dies |
|
Range of Stamping Machine |
From 25T to 300T |
The Differences between Microstamping and Typical Stamping
Microstamping, or micro metal stamping, manufactures more precise and tinier parts than traditional metal stamping. The technology and quality standards for micro part fabrication are significantly superior to ones required for standard metal stamping. Micro component manufacturing requirements for precision and tolerance are also higher in this small part stamping process, within 0.1 mm and the material workpiece is extremely thin. Layana's miniature component stamping capabilities are listed below:
|
Metal Stamping is a metal forming method that uses mechanical presses and stamping dies to convert flat metal sheets (blanking and other shaping processes) into specified dimensions, shapes, and functions. The manufacturability per part (dimension range, capable precision, and allowed features) will vary according to the complexity of the design.
What Are the Processes of Microstamping?
The first step of microstamping is the design and fabrication of the stamping die itself. The tooling used for manufacturing micro parts will perform different operations (e.g. blanking, bending, drawing, forming, etc.), which are carried out according to the precision requirement of the component.
- Micro Blanking: The cutting process to shear the metal sheet in one press stroke.
- Micro Punching: The process of creating small holes or indentations.
- Micro Bending: a manufacturing process that produces a V-shape, U-shape, Z-shape, etc.
- Micro Drawing: also known as stretching, is a process that shapes a metal sheet into a three-dimensional shape.
- Micro Deep drawing: a process that forms a deep, three-dimensional shape from a metal sheet.
- Micro Coining: used to create precise, three-dimensional shapes with different height levels on micro parts surface.
- Micro Chamfering: used to create beveled edges.
- Micro Swaging: used to generate a V-shaped feature in a tubular section, generally after micro drawing or micro deep drawing process.
- Micro Necking: used to reduce the diameter of a section in a tubular feature of a micro part.
- Micro Slotting: used to create precise micro slots.
- Micro Notching: used to create precise notches on micro parts.
- Micro Lancing: used to create precise tabs or flanges on a miniature component.
- Micro Slitting: used to create precise slits.
The Materials of Microstamping
Microstamping relies heavily on the selection of appropriate materials to achieve optimal results. The choice of material can significantly impact the quality, functionality, and durability, as well as the aesthetics, of the final product. These are some materials commonly used in microstamping and their unique properties.
Common Metallic Materials:
- Copper is exceptional in electrical and thermal conductivity, with types like C101, C102, C110, and C122 being widely used in electronic circuits and connectors. Copper is ductile and ideal for miniaturization, allowing for intricate microstamping. Alternatives include silver for better conductivity at a greater price and aluminum for a lighter option but worse electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity. The average price ranges from medium to high. Plating, such as with tin, nickel, or silver, can further enhance copper's properties by improving corrosion resistance and, in some cases, enhancing electrical and thermal conductivity, making it even more versatile in demanding applications.
- Aluminum is a lightweight and corrosion-resistant material, commonly available in series such as 1100 (pure aluminum), 5052 (aluminum-magnesium alloy), 6061 (aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloy), 7075 (aluminum-zinc alloy), and 2024 (aluminum-copper alloy). It offers good heat dissipation and is ideal for applications in aerospace, automotive, and electronic housings. Aluminum is highly suitable for miniaturization, allowing for fine features and thin walls. Potential alternatives include magnesium, which is lighter, and titanium, which is stronger but more expensive. The average price is medium.
- Brass is an alloy composed primarily of copper and zinc and offers good machinability and electrical conductivity, typically found in types like C260 and C360. It is often used in electrical components and decorative items, with high ease of miniaturization, making it suitable for complex shapes. Alternatives include bronze for higher strength and copper for better conductivity.
- Bronze is an alloy composed primarily of copper and tin, and is known for its high strength and corrosion resistance, with common types including C932 and C954. It is suitable for marine applications and bearings. While bronze can be miniaturized with precision, there are better alternatives in terms of formability and easiness. The other options are brass, which is more ductile, and stainless steel, which provides more corrosion resistance.
- Stainless Steel is valued for its excellent corrosion resistance and durability, with common types such as SUS 301, 304, 316, and 430. It is ideal for medical devices, food processing equipment, and aerospace components. Stainless steel allows for moderate to high precision in miniaturization, though it can be challenging due to its hardness. Alternatives include titanium, which is lighter but more expensive, and aluminum, which is lighter.
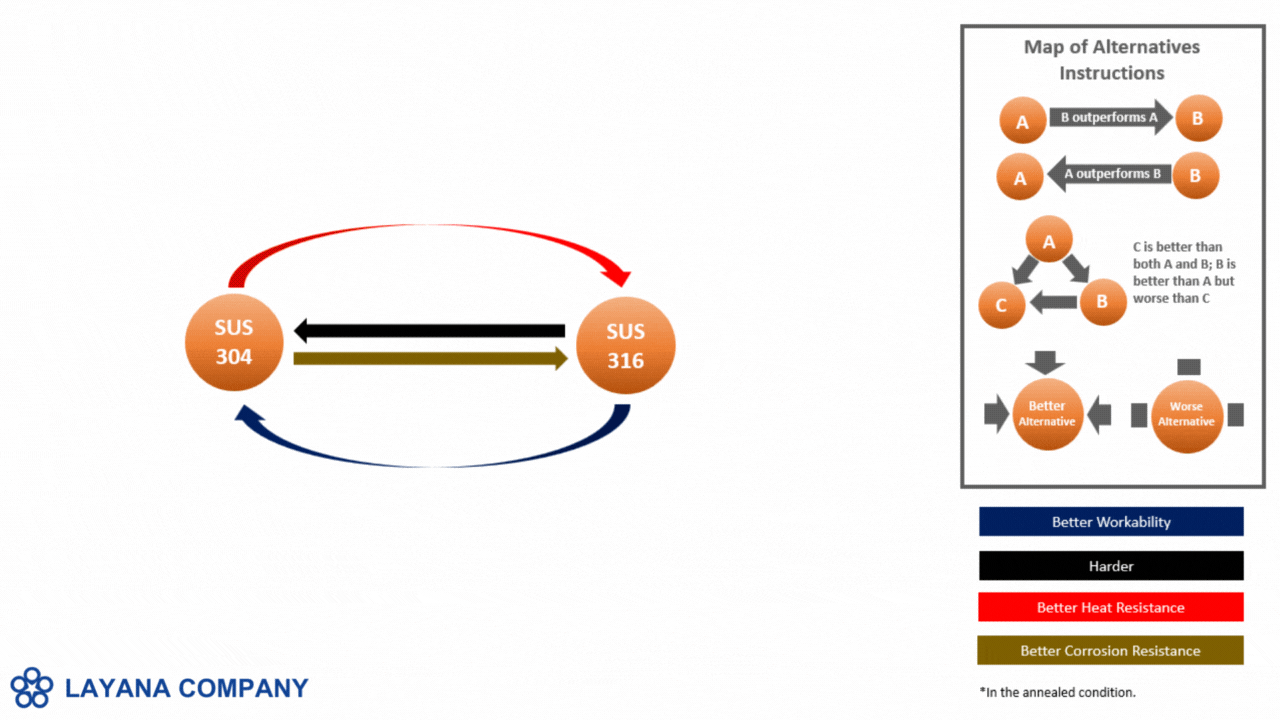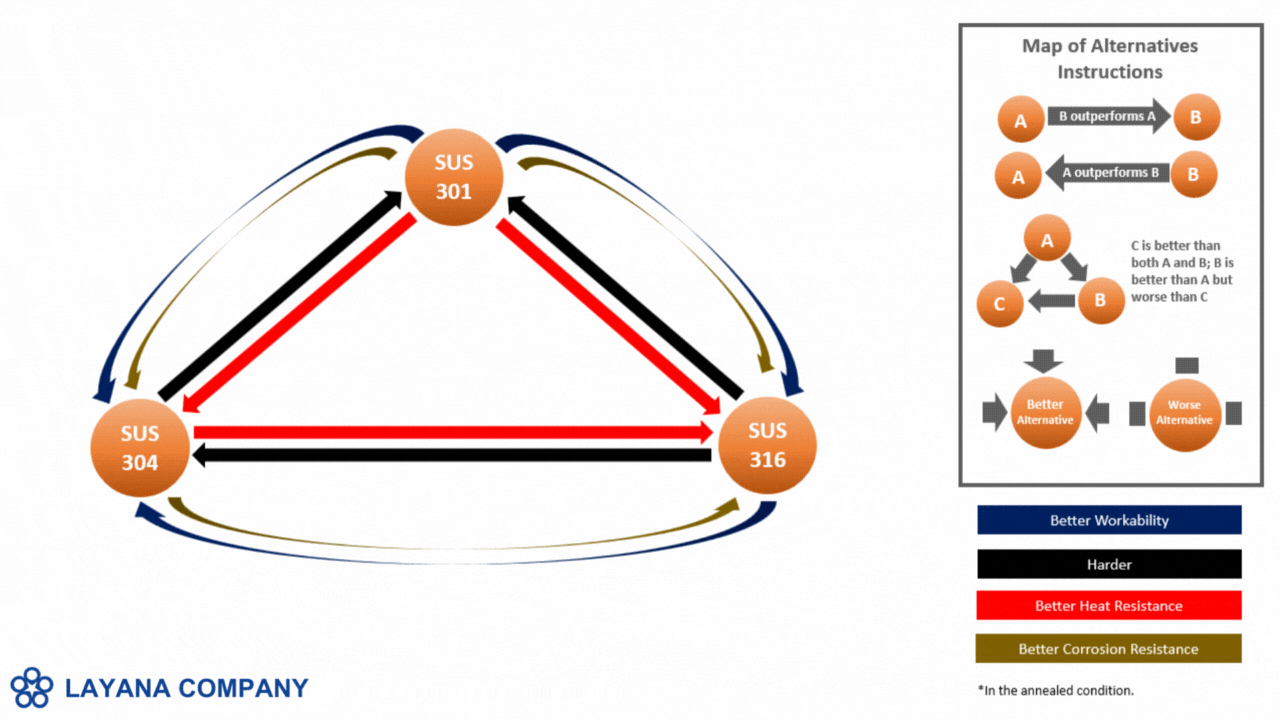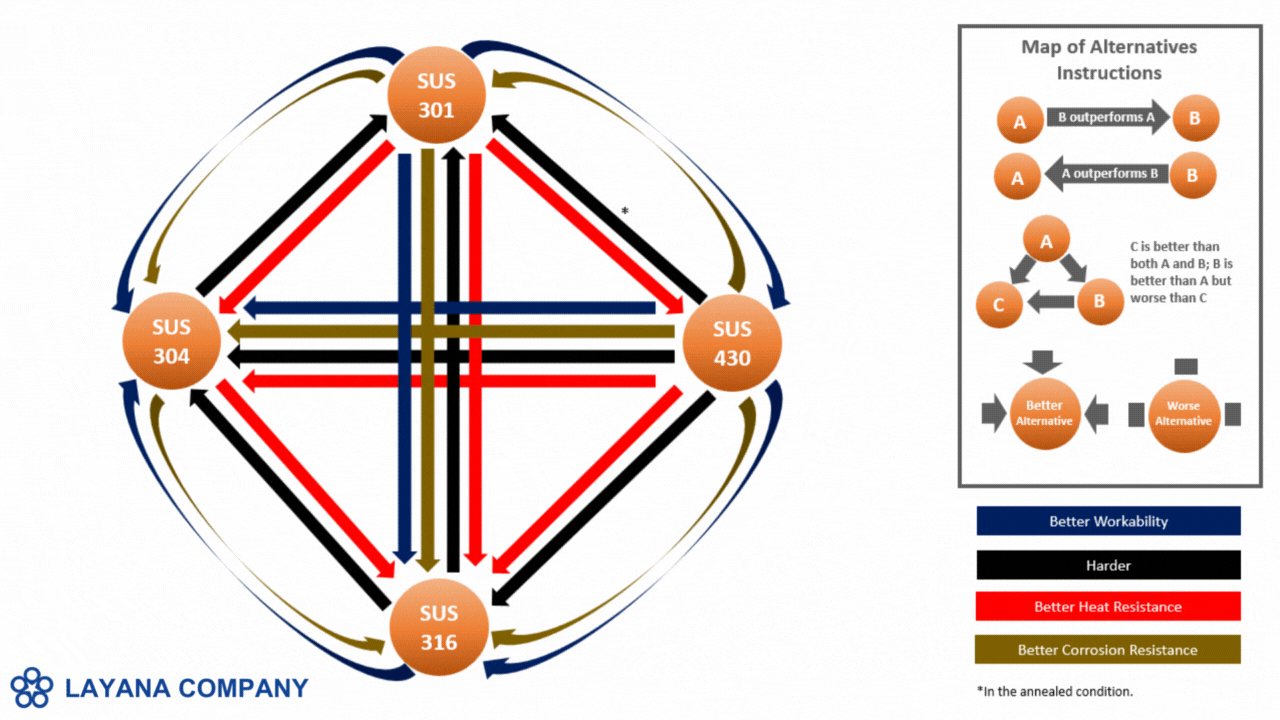
- Cold-Rolled Steel provides a high strength-to-weight ratio and is cost-effective, especially in types like 1008, 1010, and 1018. It is commonly used in structural components and enclosures. It offers moderate ease of miniaturization, suitable for strong features but less for extremely fine details. Alternatives include stainless steel for better corrosion resistance and aluminum for a lighter option.
- Titanium boasts a high strength-to-weight ratio and is biocompatible, making it suitable for medical implants and aerospace components, with common types being Grade 2 and Grade 5. It offers moderate ease of miniaturization but can be challenging to machine. Alternatives include stainless steel, which is cheaper, and aluminum, which is lighter.
Special materials:
- Beryllium Copper combines high strength with good electrical and thermal conductivity, commonly available in types like C17200 and C17510. It is often used in high-performance electronics and is excellent for micro features due to its strength and conductivity. Alternatives include phosphor bronze, which is safer and cheaper, and copper, which has better conductivity.
- Cladded Strips are customizable materials that combine the properties of different metals, making them suitable for electrical contacts and thermal management components. They offer high ease of miniaturization, allowing for complex features with tailored properties. Alternatives include pure metals or traditional alloys, depending on the application.
The Pros and Cons of Microstamping
The advantages of an automated micro stamping system include mass production, complex operation, and pressure formation capabilities which reduce labor costs, metal scraps, and the need for a secondary finishing process, respectively. The precision microstamping process leaves the micro-sized components intact, removing the need for cleanup, and the flat unblemished surface is best for electroplating and coating to increase the durability of parts. Microstamping also enables the cost-effective production of complex parts in large quantities. However, microstamping does not support small batch production due to die expenses and trial production costs, which greatly raises the unit price and is economically impractical.
The Applications of Microstamping
Micro Stamped Parts by Layana
Microstamping is particularly advantageous for the electronics industry, where the demand for miniaturization and high-performance components is ever-increasing. By employing microstamping, we can produce tiny metal parts that are essential for the functioning of PCBs, such as connectors, terminals, and contacts, with consistent quality and minimal material waste. The process is highly efficient, making it suitable for large-scale production runs. It also allows for the production of complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional stamping methods. This technology not only enhances the reliability and performance of electronic devices but also contributes to cost-effectiveness and sustainability in manufacturing. Below is a list of industries where the application of microstamping is widely used:
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Electronics
- Biotechnology
- Medical
- Optical
- Power Electronics
- Other fields
Case Study: Microstamping for PCB Components manufacturing
Below are some examples of parts that are used in PCB mounts that can be manufactured using microstamping:
- EMI/RFI Shielding Elements: These components protect electronic devices from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), and it affects the performance of the device.
- PCB Contacts: These are metallic connectors on a PCB that allow for connection and communication with other components or boards.
- PCB Connectors and Interconnectors: Devices that join sections of circuits together in PCBs, are crucial for forming reliable connections.
- PCB Miniature Springs: Small springs that are used to provide mechanical movements or electrical connections within PCB assemblies.
- PCB Shunts: Shunts in PCBs are used to allow current to pass around another point in the circuit, often used for bypassing or testing.
- PCB Ground Springs: These springs ensure a good ground connection, which is critical for the safe and proper operation of the circuit.
- PCB Brackets and Supports: These structural components hold other parts in place, providing structural integrity and resistance to mechanical stress.
- PCB Lead Frames: Used to carry signals or power within integrated circuit packaging, which are essential for connecting the silicon chip with external circuits.
- Banana Springs: Used in PCBs primarily for making temporary or reliable electrical connections in testing, prototyping, and other applications.
- Battery Contacts: These components provide an electrical connection between the battery and the device, ensuring power supply to the circuit.
- Retention Caps: Used to secure or hold other components in place, ensuring they do not move or loosen due to vibration or other mechanical forces.
- Ground Sleeves for PCB Mounts: Provide shielding and grounding to components mounted on a PCB, which is crucial for reducing electronic noise and interference.
|
|
 |
Conclusion
As technology progresses, consumer electronics design increasingly prioritizes portability and lighter weight. Products like smartphones, tablets, and memory drives now rely heavily on micro parts and require large-scale production. As a result, microstamping has become a central focus in manufacturing. The "size effect" — emphasizes the differences between producing micro components and traditional, larger parts — has further highlighted the importance of advancing microstamping techniques to meet the growing demand for these smaller, intricate parts.




