Quality
IATF 16949
The Definition of IATF 16949
IATF 16949 is a globally recognized quality management system standard specifically designed for the automotive industry. Its primary focus is on promoting continuous improvement and preventing waste and errors in the supply chain. Many automotive manufacturers worldwide have adopted IATF 16949 as their preferred global sourcing standard for automotive components, ensuring high-quality products and services that meet customer requirements and comply with legal and regulatory standards.
The Origin of IATF 16949
The origin of IATF 16949 comes from many car manufacturers establishing standard quality management systems according to their local national standards, regulations and requirements. To ensure global consistency and fairness, ISO/TS 16949 was first established and was one of the most widely used international standards in the automotive industry. It was later replaced by IATF 16949 in 2016, which redefined the quality management requirements for the automotive industry. The aim is to prevent product and service deficiencies and reduce errors and waste in the supply chain. It sets quality standards for direct suppliers who produce materials, products, service components or end services, such as heat treatment and electroplating processing.
Advantages of IATF 16949 Certification
-
Improved competitiveness:Obtaining the international standard certification of IATF 16949 helps companies gain customer trust and access to more business opportunities, thus enhancing their competitiveness.
-
Increased business value:The spirit of IATF 16949 is continuous improvement, which can increase business value and ensure sustainable company operations.
-
Prevention of product deficiencies:Following the quality management process of IATF 16949 can reduce nonconforming products and minimize internal and external failure costs.
-
Increased efficiency:Following the IATF 16949 system architecture can improve product quality and increase profitability and efficiency through appropriate management.
-
Quality assurance:Establishing 1st to 3rd-level documents and using procedural manuals to cycle through the company's overall operations in accordance with the IATF 16949 system architecture helps to increase customer satisfaction by ensuring strict quality control.
The Five Core Tools in IATF 16949
To ensure consistency and strengthen collaboration in the automotive industry supply chain, IATF 16949 provides five core tools to link quality operations in product design, process design, production, installation, and service. The five core tools are:
- APQP ─ Advanced Product Quality Planning: A structured method used to identify and establish the steps necessary to ensure customer satisfaction with a product.
- PFMEA ─ Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis: A systematic review and analysis of new/revised processes to anticipate, address, or monitor potential process issues for new/revised product projects.
- MSA ─ Measurement System Analysis: A process used to evaluate measurement units or assess measured characteristics using a set of instruments or gauges, standards, operations, methods, fixtures, software, personnel, environment, and assumptions; in other words, the entire process used to obtain measurement results.
- PPAP ─ Production Part Approval Process: A process used to determine if a supplier has understood all of the customer's engineering design records and specifications.
- SPC ─ Statistical Process Control: The use of statistical techniques, such as control charts, to analyze a process or its output, in order to take appropriate action to achieve and maintain a state of statistical control and improve process capability.
The Conditions for Obtaining IATF 16949
To understand the path to certification, it is crucial to comprehend both the conditions required for obtaining IATF 16949 certification and the steps involved in its implementation.
- Implementation of ISO 9001: Your organization needs to first implement ISO 9001 since IATF 16949 is built upon ISO 9001, with specific automotive industry requirements added. Ensure that your organization is already ISO 9001 certified.
- Quality Management System: You must establish and maintain a quality management system to ensure compliance with all requirements of the IATF 16949 standard.
- Process Analysis and Improvement: Conduct an analysis of various processes to identify potential improvement opportunities and take measures to reduce variability and enhance efficiency.
- Supply Chain Management: IATF 16949 places high demands on the supply chain. Ensure that your suppliers also comply with the relevant quality standards.
- Measurement and Analysis: Develop effective measurement and analysis processes to monitor and improve product and process performance.
- Document Control: Implement a document control process, including document version control, document reviews, and approvals.
- Risk Management: Perform a risk assessment to identify potential risks that could lead to issues and take steps to mitigate these risks.
Steps to Implement IATF 16949:
To ensure effective implementation and achieve IATF 16949 certification, it is crucial to follow a series of strategic and methodical steps.
- Understanding the IATF 16949 Standard: Your team must gain a comprehensive understanding of the requirements of the IATF 16949 standard to ensure your organization meets these requirements.
- Planning: Develop a project plan that includes resource allocation, setting a timeline, and defining tasks.
- Team Organization: Assemble a team dedicated to IATF 16949 certification, ensuring team members possess relevant knowledge and experience.
- Internal Audits: Conduct internal audits to determine if your organization complies with IATF 16949 requirements. Identify potential issues and take corrective actions.
- Employee Training: Ensure your employees understand the IATF 16949 standard and can effectively execute related tasks.
- Document Preparation: Ensure your quality management system documents meet the requirements of the IATF 16949 standard.
- External Audit: Contract a third-party auditing agency certified in IATF to perform an external audit. They will evaluate your organization's compliance with the standard.
- Corrective Actions: If issues are identified during the external audit, take corrective actions to resolve these issues.
- Certification Attainment: If your organization successfully passes the external audit, you will obtain IATF 16949 certification.
- Maintenance of Certification: Regularly conduct internal audits and maintain the quality management system to ensure ongoing compliance with the IATF 16949 standard.
History of IATF16949 Compliance at Layana
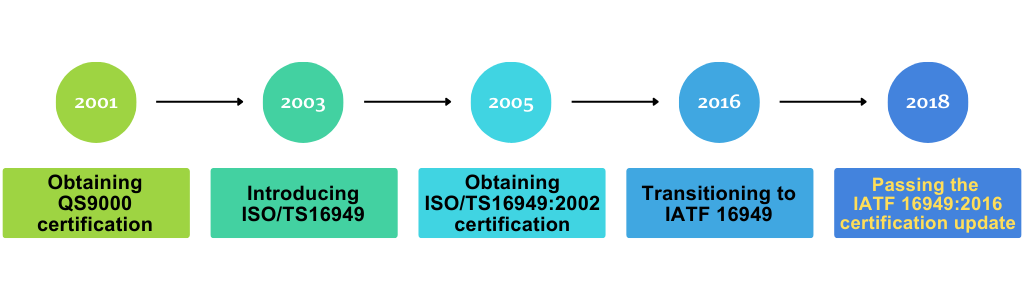
Layana is an integrated automated manufacturing factory that has been implementing IATF 16949 for over 20 years. In 2001,Layana obtained QS9000 certification and started implementing ISO/TS 16949 in 2003, obtaining ISO/TS16949:2002 certification in 2005. To this day, LAYANA has continuously used IATF 16949, having converted to it in 2016. When the Lukang headquarters was completed in 2018, the IATF 16949:2016 certification was also successfully obtained.
| IATF 16949 Product Quality System Update - Supplementary Course | IATF 16949 Product Quality System Update - Internal Audit | IATF 16949:2016 Quality Training |
Conclusion
Only high standards of quality certification and inspection can create the best product quality.
For the past 41 years, LAYANA has focused on manufacturing technologies such as metal stamping, plastic injection, plastic over-molding, and automated production. The company has always implemented its quality management system in accordance with the international standard of IATF 16949, and uses a scientifically-guided management approach to fulfill its quality commitments to customers. The company slogan " TQM comes from good working attitude and character " is deeply rooted in Layana's DNA.
Read more about quality
Six Sigma
Quality Control Circle
In today's competitive business landscape, ensuring the highest quality of products and services is paramount. One tool that has revolutionized the quest for quality improvement is the Quality Control Circle (QCC). Originating in Japan, QCC has grown into a global phenomenon, offering organizations a structured approach to enhance quality and achieve excellence. This article delves deep into the world of QCC, exploring its origins, definitions, methodologies, steps, benefits, and extensive applications.
The Origins of QCC
Quality Control Circles, often abbreviated as QCC, owe their origins to Japan's dynamic manufacturing sector in the 1960s. Faced with fierce competition, Japanese companies sought innovative ways to elevate production efficiency and product quality. In this milieu, the concept of QCC emerged. Some of Japan's industrial giants, including Toyota, played pivotal roles in introducing and promoting QCC as an effective strategy for enhancing quality.
What is QCC?
QCC is a team-based quality improvement methodology founded on the principle of harnessing the creative potential and expertise of internal team members. The core idea is to achieve consistent and gradual enhancements in product and process quality. Within the QCC framework, employees are empowered to take an active role in addressing quality issues, fostering an environment that encourages collaboration and innovation.
The Methodology of Using QCC
The heart of the QCC methodology lies in the formation of small, cross-functional teams comprising members from diverse departments and functions. This diversity ensures the exchange of a wide array of perspectives and professional knowledge. The team embarks on a journey by first identifying a quality issue that requires improvement. Subsequently, through brainstorming and extensive discussions, the team collaboratively devises solutions. These solutions are then implemented with continuous monitoring to ensure their feasibility and effectiveness.
Steps in Implementing QCC
The implementation of QCC can be elucidated through a series of key steps:
- Identify the Issue: The QCC team pinpoints a quality issue, typically associated with a product or process.
- Gather Data: Pertinent data is meticulously collected and analyzed to grasp the nature and implications of the problem.
- Develop Solutions: The team generates multiple solutions and chooses the most suitable one to rectify the issue.
- Implement Improvements: The chosen solution is set into motion, and the team diligently tracks its progress.
- Evaluate Results: An assessment is conducted to gauge the effectiveness of the improvements and determine if they align with the expected outcomes.
- Share Experiences: Knowledge and methodologies garnered from the improvements are disseminated among other teams, propelling organizational learning and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
The Benefits of QCC
Quality Control Circles offer a plethora of benefits, including:
- Quality Enhancement: QCC, through continuous improvement, augments the quality of products and processes, leading to heightened customer satisfaction.
- Employee Engagement: QCC encourages active employee participation, bolstering their sense of belonging and involvement.
- Problem Resolution: QCC teams effectively tackle existing issues, resulting in fewer defects and errors.
- Efficiency Improvement: QCC optimizes processes, reducing waste and redundant work, thereby enhancing efficiency.
- Team Collaboration: Teamwork across different departments fosters collaboration, shattering information silos.
The Applications of QCC
The applications of QCC span across diverse industries, extending well beyond manufacturing. Sectors such as services, healthcare, and education have also embraced QCC methodologies to elevate quality standards. Regardless of an organization's scale or nature, QCC can be adapted and employed to suit specific circumstances.
The Example of QCC Applications
To illustrate the real-world impact of QCC, let's delve into some practical examples:
- Automotive Manufacturing
In an automotive manufacturing facility, QCC teams systematically identified and addressed issues related to product defects, resulting in reduced recalls and higher customer satisfaction. - Healthcare
Hospitals and healthcare institutions employ QCC to enhance patient care processes, reducing errors, and improving overall healthcare quality. - Education
In the field of education, QCC is utilized to streamline administrative processes, leading to increased efficiency and improved student experiences.
QCC: A Global Phenomenon
Quality Control Circles have transcended geographical boundaries and cultural differences to become a global phenomenon. Organizations worldwide recognize the power of QCC in driving continuous improvement and achieving excellence.
Our Latest QCC Presentation in 2025
|
The 34th QCC Presentation |
|
QCC Presentation in 2024
|
The 31st QCC Presentation |
The 32nd QCC Presentation |
The 33rd QCC Presentation |
Read More About Our Past QCC Presentations
Conclusion
In conclusion, Quality Control Circles represent a powerful methodology for organizations seeking to enhance their products, processes, and services. Whether in manufacturing or other industries, the QCC approach consistently delivers on its promise of fostering a culture of quality excellence. The success of QCC lies not only in its technical and process-oriented aspects but also in its ability to empower employees and harness their creativity, ultimately propelling organizations toward sustained quality improvement.
With the ever-increasing focus on quality in today's competitive markets, QCC remains a valuable tool for organizations striving to meet and exceed customer expectations. As the global business landscape continues to evolve, QCC is poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of quality management.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma Definition
Six Sigma is a data-driven quality management methodology aimed at minimizing process or product variability to the maximum extent. It is based on statistical principles, striving for no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities over an extended period. This approach emphasizes data collection, analysis, and improvement to ensure process stability and consistency.
Six Sigma Application Environment
Six Sigma is applicable to various organizations and industries, including manufacturing, services, healthcare, and finance. It can be applied to production processes, supply chain management, product design, customer service, and various decision-making processes. Regardless of the organization's size, as long as there is complexity and variability, Six Sigma can provide a path for continuous improvement.
Benefits of Using Six Sigma
- Improving Quality: The primary goal of Six Sigma is to reduce the defect rate, thereby enhancing the quality of products and services. Through data analysis and improvement, organizations can better meet customer expectations and reduce the occurrence of quality issues.
- Enhancing Efficiency: Reducing variability contributes to improved process efficiency. The Six Sigma methodology helps organizations identify and eliminate waste, reduce cycle times, and enhance production capacity.
- Reducing Costs: By decreasing the defect rate and improving efficiency, Six Sigma helps organizations reduce production costs. This includes reducing waste, lowering maintenance expenses, and increasing resource utilization.
- Boosting Customer Satisfaction: By delivering higher-quality products and services, organizations can increase customer satisfaction, enhance customer loyalty, and ultimately gain a larger market share.
DMAIC Methodology in Six Sigma
- Define: In this stage, the project's goals, scope, and key performance indicators (KPIs) are determined. A clear definition of the problem is crucial for the project's success.
- Measure: Relevant data is collected, and the current process performance is analyzed. This stage helps understand the process's baseline and identify existing issues.
- Analyze: Statistical tools and techniques are employed to identify potential root causes, explaining why the problem occurs. This ensures that the solutions are targeted.
- Improve: In this stage, improvement plans are developed and implemented to reduce variability, enhance quality, and efficiency. The best solution is selected, and pilot tests are conducted.
- Control: The control phase aims to ensure ongoing improvement and prevent problems from recurring. Monitoring measures are implemented, and processes are standardized to maintain the improvement's effectiveness.
DMADV Methodology in Six Sigma
- Define: Determine the goals and customer requirements for the product or service. Clearly outline the project scope and objectives.
- Measure: Collect and analyze data about the existing process and product to establish performance benchmarks.
- Analyze: Determine the root causes of the problem by analyzing data, providing a foundation for the design phase.
- Design: Develop a new product or service design based on previous analysis. This includes engineering design, process design, etc.
- Verify: Ensure that the new design meets customer requirements and achieves the expected performance level through testing and evaluation.
Six Sigma Certification Levels
In Six Sigma, there are different levels of certification to denote an individual's training and experience:
- White Belt: White Belts typically receive basic awareness training in Six Sigma within the organization. While they may not directly engage in projects, they have a basic understanding of Six Sigma principles and methods. White Belts play a supportive role in Six Sigma projects, spreading knowledge and assisting with data collection and analysis. They may participate in project teams and contribute significantly to the team.
- Green Belt: Green Belts receive more in-depth Six Sigma training and often serve in support roles within project teams. They possess higher levels of knowledge and skills and can be more directly involved in project implementation. Green Belts are typically responsible for specific aspects of a project, using Six Sigma tools for data analysis, root cause identification, and improvement planning. They play crucial roles in project teams.
- Black Belt: Black Belts are experts who have undergone extensive training and accumulated experience in Six Sigma. They usually lead Six Sigma project teams and are responsible for comprehensive project management, including problem definition, data collection, analysis, development and implementation of improvement plans, and monitoring and control. Black Belts possess advanced statistical and analytical skills, capable of addressing complex issues and driving improvement. They often coordinate multiple projects and hold leadership positions within the organization.
- Master Black Belt: Master Black Belts are senior professionals who often take on leadership and training roles within the organization. They have profound knowledge and experience and can guide multiple projects and teams. Master Black Belts play a critical role in disseminating and implementing the Six Sigma methodology. They train and mentor other Black Belts and Green Belts and help build a Six Sigma culture within the organization.
- Diamond Belt: The Diamond Belt is the highest level of Six Sigma certification, representing exceptional knowledge and leadership abilities in the field. Diamond Belts are typically strategic decision-makers and consultants, providing advanced strategic guidance to the organization. They possess extensive knowledge and experience, capable of addressing complex problems and driving strategic change within the organization.
Different levels of certification ensure that the organization has the appropriate skills and knowledge to drive Six Sigma projects and achieve quality improvement objectives. Organizations can train and certify their employees based on their needs and goals to ensure they have the right roles and capabilities in Six Sigma projects.
Layana's Six Sigma Certification Levels
![six sigma 2020]()
| Ranking | Personnel | |
|---|---|---|
| Champion | 1 | Layard Lai |
| Master Black Belts | 3 | Penny Lin (General Manager), TN Chen (Vice GM), Mike Lai (President-CN) |
|
Black Belt |
11 |
Alex Lai (President-TW), Jenny Yang (Consultant), Carrie Yao (Vice GM), Ming-Jie Shih (MFG Manager), Jack Lee (Manager), Mark Chen (Manager), Molly Yang (Manager), Debbie Shih (Manager), Jian-Yao Yang (R&D Vice GM), Shr-Chin Lee (Manager), Yi-Hsin Chen (Manager) |
|
Green Belts |
12 | David Chen (Assistant Manager), Amanda LU(Assistant Manager), Sophia Yeh (Assistant Manager), Bonnie Lai (Assistant Manage), Cheng-Du Lin (Assistant Manager), Ming-Hong Guo (Assistant Manage), Ji-Shan Sun (Section Manager), Shun-Yang Chang (Assistant Manager), Yu-Neng Chen (Facility Engineer),Yi-Ren You (Supervisor), Yao-cheng Yang (Supervisor), Wei-Lun Zhang (specialist) |
Conclusion
Six Sigma is a powerful quality management methodology that can help organizations improve quality, reduce costs, enhance efficiency, and increase customer satisfaction. Through the DMAIC method, organizations can identify issues, find root causes, and implement continuous improvement. Furthermore, different levels of certification (Green Belt, Black Belt, White Belt, Master Black Belt, and Diamond Belt) ensure that organizations have qualified individuals to drive this process.
|
|
2024 Seventeenth Six Sigma Project EventThe 2024 Sixth Standard Deviation Project was held on January 19th. |
|
|
2023 Sixteenth Six Sigma Project EventSince 2000, Layana has been using Six Sigma projects for improvement, addressing long-standing issues in our work. The core values of "Pursuing Excellence, Stopping at Perfection" lie in quality and cultural ideals. We must uphold the spirit of Six Sigma, continually innovate, and strive for excellence. Through years of experience in various products, including parts manufacturing, we seek mutual development with our customers, aiming to achieve excellence and continuous improvement. |
| 2021 | Fifteenth Six Sigma Improve Project Event |
|
2020 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
Twelfth Six Sigma Improve Project Event |
|
2015 Tenth Six Sigma Improve Project Event |
2016 Eleven Six Sigma Improve Project Event |
|
2013 Eighth Six Sigma Improve Project Event |
2014 Ninth Six Sigma Improve Project Event |
|
2012 |
Taiwan Training Quality System Silver Prize granted |
|
2010 |
SPC was implemented |
|
2007 |
ISO9001 Certificate of Design and Manufacture of Flatware granted in November. |
|
2006 |
5S coached by China Productivity Center in March. |
|
2005 |
ISO/TS16949:2002 certified. Third Six Sigma Project Event in Kaohsiung. ERP System implemented in August. |
|
2004 |
Second Six Sigma Project Event in Taichung. Six Sigma methods coached by China Productivity Center in March. |
|
2003 |
First Six Sigma Project Event in Taipei. ISO/TS16949:2002 Implementation coached by Kind Consulting in November. |
|
2002 |
TPS/Lean techniques implemented to eliminate Seven Wastes. |
|
2001 |
QS-9000 was implemented |
|
2000 |
Six Sigma Training Courses was launched |
Training Programs
Education & Training at Layana
Layana believes in empowering its employees through lifetime learning.
A certain percentage of the annual revenue is dedicated to education and training programs. Layana runs routine in-house programs of Six Sigma, IATF 16949, quality circles, and TPS consultant programs. Employees are also encouraged to study at domestic universities or abroad. As a company policy, employees who obtain a college degree or professional certifications will get a salary raise and monetary rewards.
What Kind of Trainings Layana Has?
- SPC-Statistical Process Control
-
MSA-Measurement Systems Analysis
-
FMEA-Potential Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
-
APQP-Advanced Product Quality Planning
-
PPAP-Production Part Approval Process
-
Small-Group Education Training in each Department
Awards and Recognition
Since day one we have strived to be the customer-centric company. We’re honored to be recognized for the work we do on behalf of our customers, employees, and communities around the world. Here are some recent awards we’ve received.
- Happy Corporate: Layana COMPANY Honored with the 3 Star Awards, 2016
- Molex 2015 Best in Class” medal, 2016
- 2015 Taiwan Continuous Improvement Award (Central District President's Award)
- Aawarded Silver Tower Prize, 2015
- Taiwan Train Quality System, 2012
|
Happy Corporate:3 Star |
Molex Best in Class medal |
Taiwan Continuous Improvement |
Silver Tower Prize |
TTQS |
Skills training opportunities for employees
The customer is at the heart of everything we do. Layana is a place where smart, passionate people obsess over customers and innovate on their behalf.
|
ERP/CQT/CQE/PMP Licenses |
Technical Research Seminar |
Morning Meeting |
Working at Layana
We listen to our employees and innovate to keep each of them healthy and safe while they are at work...
|
On-the-Job Training |
Technical Apprenticeship Program |
New Leadership Principles |
Our Programs
In our daily work, each person is supposed to propose improving projects and to solve problems virtually. We are all trained to become problem solvers. "We want to be better than better." This working philosophy makes improvements possible and probable.
|
5Whys Training |
TQM,TPM,TPS,Lean Six Sigma |
5S |
Quality Inspection
Robust Quality Control
With superior quality assurance, Layana provides our customers with high-quality products
Layana, IATF 16949 and ISO 50001 certified company, has a designed high-level Precision Measuring Room in the house, with temperature and cleanliness control.
We have a dedicated inspection team with professional automated quality control equipment, including Zeiss CMM, Micro Vu, Keyence, etc. measuring instruments for product inspection, measurement, and test, to enhance our efficiency on quality control. Support our customers in multiple industries, such as automotive, electronics, medical, optical, power module, aerospace, etc. with modern measuring and inspection technology.
Highest quality control in each stage, from IQC, IPQC, OQC, of course traceable, measurable, and documented
- SPC Software System
- Automated Inspection
- Precision Measuring
- Barcode/ Labelling Management, for Traceability
- Calibration
- PPAP, CPK, Capability Study, Test Report
Inspection & Testing Equipment
|
Description (Inspection & Testing Equipment) | |
|---|---|
|
1. ZEISS CMM Contura RDS |
2. HITACHI XRF Spectrometer |
|
3. Micro-Vu Video Measuring System |
4. Keyence Image Dimension Measuring System |
|
5. TOMAS 2.5D Video Inspection System |
6. Giant Force Salt Spray/Mist/Humidity Corrosion Tester |
|
7. Future-Tech Vickers Hardness Tester |
8. Mitutoyo Rockwell Hardness Tester |
|
9. MITUTOYO Roughness tester |
10. TOADK Super insulation meter |
|
11. Glass Dial Series-Optical Inspection Sorting Machine |
12. H.T. Pull Force Testers |
|
13. KETT Infrared Moisture Analyzer |
14. Fischer handheld coating thickness Tester |
Inspection Equipment
|
ZEISS CMM Contura RDS |
HITACHI XRF Spectrometer |
Giant Force Salt Spray/Mist/Humidity Corrosion Tester |
|
KEYENCE Image Dimension Measurement System |
Glass Dial Series-Optical Inspection |
Small Automatic Metallographic Cutting Machine |
|
Small Automatic Metallographic Cutting Machine |
Automatic Metallographic Inlay Machine |
Manual Metallographic Grinding & Polishing Machine |
Quality Assurance
Layana, guided by the paramount principle of prioritizing quality, comprehensively manages and controls quality in all aspects, including personnel, the environment, supply chain, and products. Upholding the belief in continuous improvement, Layana strives to enhance overall quality and efficiency. Through the collective efforts of all team members and collaborative cooperation, the quality standards not only meet but exceed customer requirements.
To achieve this quality policy, we base our approach on the requirements of the IATF 16949:2016 Automotive Quality Management System. With input from all team members on matters of quality, we revise and establish departmental quality objectives and implement various standard operating procedures. We continuously improve and ensure the execution of our company's quality management system, aligning with the concept of sustainable business operations.
Layana operates its quality management system based on IATF 16949, with the following methods for continuous improvement and implementation of various quality management systems:
- Education and training:arrange IATF 16949 quality training courses to strengthen all employees' concepts and applications of the five core tools.
- Internal audits:each department consolidates operational related indicators and schedules internal audits for IATF 16949 to verify whether the system is being implemented correctly. If problems are discovered, corrective actions are taken, and root cause analysis and improvement measures are proposed to maintain the effectiveness of all operations in IATF 16949.
- Supplier audits:conduct system, process, and product audits for the top five suppliers and regularly assess their supply level to ensure that customer requirements are met.
- Equipment calibration:schedule instrument calibration and execute measurement system analysis (MSA) to analyze the variation and characteristics of the measurement system, ensuring the reliability of instruments and product quality.
- Customer satisfaction:survey customer satisfaction and understand the gap between their needs and expectations. Optimize areas of dissatisfaction to meet customer needs and achieve the company's sustainable business goals.
- Standard development:develop quality inspection standards and continuously optimize rules to implement checks on all inspection processes, ensuring that quality meets customer requirements.
- Continuous improvement:through departmental team discussions, stimulate brainstorming and analysis using various tools to meet customer requirements.
Layana's Quality Management System
- APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning)
- Control Plan
- PFMEA (Potential Failure Mode and Effects Analysis)
- PPAP Checklist
- MSA (Measurement System Analysis)
- SPC (Statistical Process Control)
- GR&R (Gage R&R)
- Supplier ISO certifications
- Six Sigma
- 6S (5S + Safety)
|
ISO 50001 Energy Management System |
Green Building (Gold Level) |
